我们知道Fibonacci数列,现在我们来求一个Fib数模n的循环节的长度。
对于一个正整数n,我们求Fib数模n的循环节的长度的方法如下:
(1)把n素因子分解,即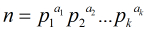 (2)分别计算Fib数模每个
(2)分别计算Fib数模每个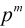 的循环节长度,假设长度分别是
的循环节长度,假设长度分别是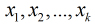 (3)那么Fib模n的循环节长度
(3)那么Fib模n的循环节长度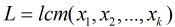
从上面三个步骤看来,貌似最困难的是第二步,那么我们如何求Fib模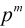 的循环节长度呢?
这里有一个优美的定理:Fib数模
的循环节长度呢?
这里有一个优美的定理:Fib数模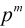 的最小循环节长度等于
的最小循环节长度等于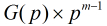 ,其中
,其中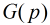 表示Fib数模素数
表示Fib数模素数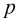 的最小循环节长度。可以看出我们现在最重要的就是求
的最小循环节长度。可以看出我们现在最重要的就是求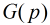 对于求
对于求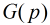 我们利用如下定理:
如果5是模
我们利用如下定理:
如果5是模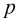 的二次剩余,那么循环节的的长度是
的二次剩余,那么循环节的的长度是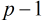 的因子,否则,循环节的长度是
的因子,否则,循环节的长度是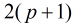 的因子。
的因子。
顺便说一句,对于小于等于5的素数,我们直接特殊判断,loop(2)=3,loop(3)=8,loop(5)=20。
那么我们可以先求出所有的因子,然后用矩阵快速幂来一个一个判断,这样时间复杂度不会很大。
模板代码:
对于一个正整数n,我们求Fib数模n的循环节的长度的方法如下:
(1)把n素因子分解,即
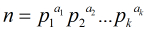 (2)分别计算Fib数模每个
(2)分别计算Fib数模每个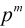 的循环节长度,假设长度分别是
的循环节长度,假设长度分别是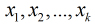 (3)那么Fib模n的循环节长度
(3)那么Fib模n的循环节长度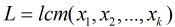
从上面三个步骤看来,貌似最困难的是第二步,那么我们如何求Fib模
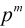 的循环节长度呢?
这里有一个优美的定理:Fib数模
的循环节长度呢?
这里有一个优美的定理:Fib数模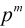 的最小循环节长度等于
的最小循环节长度等于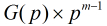 ,其中
,其中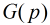 表示Fib数模素数
表示Fib数模素数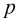 的最小循环节长度。可以看出我们现在最重要的就是求
的最小循环节长度。可以看出我们现在最重要的就是求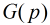 对于求
对于求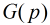 我们利用如下定理:
如果5是模
我们利用如下定理:
如果5是模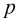 的二次剩余,那么循环节的的长度是
的二次剩余,那么循环节的的长度是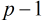 的因子,否则,循环节的长度是
的因子,否则,循环节的长度是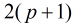 的因子。
的因子。
顺便说一句,对于小于等于5的素数,我们直接特殊判断,loop(2)=3,loop(3)=8,loop(5)=20。
那么我们可以先求出所有的因子,然后用矩阵快速幂来一个一个判断,这样时间复杂度不会很大。
模板代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
const int M = 2;
struct Matrix
{
LL m[M][M];
};
Matrix A;
Matrix I = {1,0,0,1};
Matrix multi(Matrix a,Matrix b,LL MOD)
{
Matrix c;
for(int i=0; i>= 1;
p = multi(p,p,MOD);
}
return ans;
}
LL gcd(LL a,LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
const int N = 400005;
const int NN = 5005;
LL num[NN],pri[NN];
LL fac[NN];
int cnt,c;
bool prime[N];
int p[N];
int k;
void isprime()
{
k = 0;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(int i=2; i>= 1;
a = a * a % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL legendre(LL a,LL p)
{
if(quick_mod(a,(p-1)>>1,p)==1) return 1;
else return -1;
}
void Solve(LL n,LL pri[],LL num[])
{
cnt = 0;
LL t = (LL)sqrt(1.0*n);
for(int i=0; p[i]<=t; i++)
{
if(n%p[i]==0)
{
int a = 0;
pri[cnt] = p[i];
while(n%p[i]==0)
{
a++;
n /= p[i];
}
num[cnt] = a;
cnt++;
}
}
if(n > 1)
{
pri[cnt] = n;
num[cnt] = 1;
cnt++;
}
}
void Work(LL n)
{
c = 0;
LL t = (LL)sqrt(1.0*n);
for(int i=1; i<=t; i++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
if(i * i == n) fac[c++] = i;
else
{
fac[c++] = i;
fac[c++] = n / i;
}
}
}
}
LL find_loop(LL n)
{
Solve(n,pri,num);
LL ans=1;
for(int i=0; i>n)
cout<
典型题目
题目一:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3977
题目二:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=5075
题目三:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3978
题目四:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4291
上面的题目一和题目二基本上是模板题,没有什么可以说的。对于第三题和第四题,我们可以看出题目四实际上是
题目三的简单版,都是一层一层找循环节,我们找出每一层的循环节后即可解决。
下面给出题目三的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int M=2;
struct Matrix
{
LL m[M][M];
};
Matrix per= {1,0,0,1};
Matrix multi(Matrix a,Matrix b,LL MOD)
{
Matrix c;
int i,j,k;
for(i=0; i>=1;
p=multi(p,p,MOD);
}
return ans;
}
LL gcd(LL a,LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=1;
a%=m;
while(b)
{
if(b&1)
{
ans=ans*a%m;
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=a*a%m;
}
return ans;
}
//勒让德符号
int legendre(int a,int p)
{
if(quick_mod(a,(p-1)>>1,p)==1) return 1;
else return -1;
}
const int N=1000005;
const int NN=50005;
bool prime[N];
int p[N];
int num[NN],pri[NN];
int num1[NN],pri1[NN];
int arr[NN];
int loop[N];
int k,cnt,c;
void isprime()
{
k=0;
int i,j;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(i=2; i1)
{
pri[cnt]=n;
num[cnt]=1;
cnt++;
}
}
void dfs(int dept,int product=1)
{
if(dept==cnt)
{
arr[c++]=product;
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<=num1[dept]; i++)
{
dfs(dept+1,product);
product*=pri1[dept];
}
}
int find_loop(int n)
{
find(n,pri,num);
int cnt1=cnt;
LL ans=1;
for(int i=0; i=0; i--)
{
MOD=loop[i];
ans=power(A,t,MOD);
ret=(ans.m[1][0]+ans.m[1][1])%MOD;
t=ret;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
isprime();
int T,n,k,p,tt=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&p);
printf("Case #%d: %d
",tt++,work(n,k,p));
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://www.51nod.com/onlineJudge/questionCode.html#!problemId=1195
分析:由于本题数据特别多,开始一直TLE,后来发现矩阵乘法里面如果取模太多会导致速度变得很慢,以前POJ上
的一道题关于矩阵求和也是因为这个TLE,尽量减少一些取模,速度会有几十倍甚至几百倍的提升。
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include