写在前面的话
本文主要分析MO(去电)的流程,研究的代码是Android 6.0的,目前只关注应用层,以GSM为例。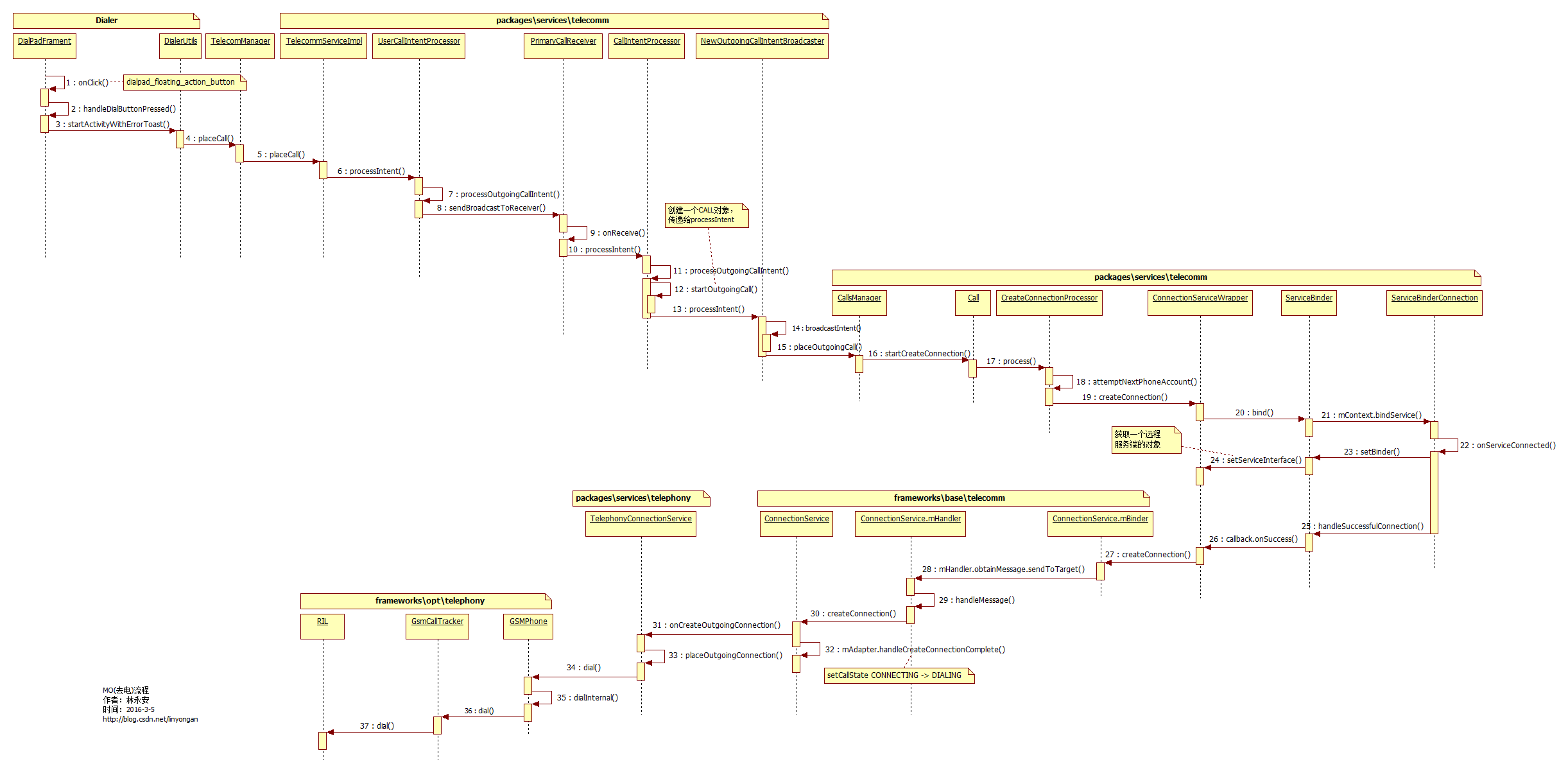 (如果图片看不清的话,可以右键选择在新标签中打开图片,或者把图片另存到自己电脑再查看。)
(如果图片看不清的话,可以右键选择在新标签中打开图片,或者把图片另存到自己电脑再查看。)
步骤1:当用户点击拨号键盘按钮(DialtactsActivity的floating_action_button),弹出拨号盘,输入完电话号码,再点击拨号按钮,此时打电话的流程开始,因此打电话流程的入口就在DialpadFragment.java(packagesappsdialersrccomandroiddialerdialpad)的onClick()方法
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.dialpad_floating_action_button:
mHaptic.vibrate();
handleDialButtonPressed();
...
}
步骤2:在handleDialButtonPressed()方法里,会先判断用户是否已输入号码,假如号码为空,则调用handleDialButtonClickWithEmptyDigits()方法显示上一次拨打过的号码。然后第一次获取到要拨打的number,在这里可以对number做一些判断或者自定义处理。
步骤11,12:在CallIntentProcessor.java的processOutgoingCallIntent()方法里,调用Call call = callsManager.startOutgoingCall(handle, phoneAccountHandle, clientExtras); (这就是Call对象的来源),最后传递给NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster。 步骤13:在NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster.java的processIntent()方法里,第二次获取到要拨打的number,这里也是对number进行一些定制操作的好地方。在这里会调用isPotentialEmergencyNumber()方法判断number是否是潜在的紧急号码,如果是紧急号码会直接走步骤15。
/**
* Processes the supplied intent and starts the outgoing call broadcast process relevant to the
* intent.
*
* This method will handle three kinds of actions:
*
* - CALL (intent launched by all third party dialers)
* - CALL_PRIVILEGED (intent launched by system apps e.g. system Dialer, voice Dialer)
* - CALL_EMERGENCY (intent launched by lock screen emergency dialer)
*
* @return {@link DisconnectCause#NOT_DISCONNECTED} if the call succeeded, and an appropriate
* {@link DisconnectCause} if the call did not, describing why it failed.
*/
int processIntent() {
...
//第二次获取到number
String number = PhoneNumberUtils.getNumberFromIntent(intent, mContext);
//判断是不是EmergencyNumber
final boolean isPotentialEmergencyNumber = isPotentialEmergencyNumber(number);
Log.v(this, "isPotentialEmergencyNumber = %s", isPotentialEmergencyNumber);
// True for certain types of numbers that are not intended to be intercepted or modified
// by third parties (e.g. emergency numbers).
boolean callImmediately = false;
if (Intent.ACTION_CALL.equals(action)) {
if (isPotentialEmergencyNumber) {
if (!mIsDefaultOrSystemPhoneApp) {//拦截第三方软件拨打的紧急号码
Log.w(this, "Cannot call potential emergency number %s with CALL Intent %s "
+ "unless caller is system or default dialer.", number, intent);
launchSystemDialer(intent.getData());//弹出系统拨号盘
return DisconnectCause.OUTGOING_CANCELED;
} else {
callImmediately = true;//紧急电话的标志
}
}
} else if (Intent.ACTION_CALL_EMERGENCY.equals(action)) {
if (!isPotentialEmergencyNumber) {//拦截在紧急拨号盘拨打的非紧急电话
Log.w(this, "Cannot call non-potential-emergency number %s with EMERGENCY_CALL "
+ "Intent %s.", number, intent);
return DisconnectCause.OUTGOING_CANCELED;
}
callImmediately = true; //紧急电话的标志
} else {
Log.w(this, "Unhandled Intent %s. Ignoring and not placing call.", intent);
return DisconnectCause.INVALID_NUMBER;
}
if (callImmediately) {//处理紧急号码
Log.i(this, "Placing call immediately instead of waiting for "
+ " OutgoingCallBroadcastReceiver: %s", intent);
String scheme = isUriNumber ? PhoneAccount.SCHEME_SIP : PhoneAccount.SCHEME_TEL;
boolean speakerphoneOn = mIntent.getBooleanExtra(
TelecomManager.EXTRA_START_CALL_WITH_SPEAKERPHONE, false);
int videoState = mIntent.getIntExtra(
TelecomManager.EXTRA_START_CALL_WITH_VIDEO_STATE,
VideoProfile.STATE_AUDIO_ONLY);
mCallsManager.placeOutgoingCall(mCall, Uri.fromParts(scheme, number, null), null,
speakerphoneOn, videoState);//快速处理紧急电话,但是并不return。
// Don't return but instead continue and send the ACTION_NEW_OUTGOING_CALL broadcast
// so that third parties can still inspect (but not intercept) the outgoing call. When
// the broadcast finally reaches the OutgoingCallBroadcastReceiver, we'll know not to
// initiate the call again because of the presence of the EXTRA_ALREADY_CALLED extra.
}
Log.i(this, "Sending NewOutgoingCallBroadcast for %s", mCall);
//普通电话走这里
if (isSkipSchemaParsing) {
broadcastIntent(intent, handle.toString(), !callImmediately);
} else {
broadcastIntent(intent, number, !callImmediately);
}
return DisconnectCause.NOT_DISCONNECTED;
}
步骤15:在这里调用了 /**
* Attempts to issue/connect the specified call.
*
* @param handle Handle to connect the call with.
* @param gatewayInfo Optional gateway information that can be used to route the call to the
* actual dialed handle via a gateway provider. May be null.
* @param speakerphoneOn Whether or not to turn the speakerphone on once the call connects.
* @param videoState The desired video state for the outgoing call.
*/
void placeOutgoingCall(Call call, Uri handle, GatewayInfo gatewayInfo, boolean speakerphoneOn,
int videoState) {
//判断是不是紧急电话
boolean isEmergencyCall = TelephonyUtil.shouldProcessAsEmergency(mContext,
call.getHandle());
……
if (isEmergencyCall) {
// Emergency -- CreateConnectionProcessor will choose accounts automatically
call.setTargetPhoneAccount(null);
}
if (call.getTargetPhoneAccount() != null || isEmergencyCall) {
if (!isEmergencyCall) {
updateLchStatus(call.getTargetPhoneAccount().getId());
}
// If the account has been set, proceed to place the outgoing call.
// Otherwise the connection will be initiated when the account is set by the user.
call.startCreateConnection(mPhoneAccountRegistrar);
} }
}
步骤16: call实例被传送到这里,终于派上用场了,进入 /**
* Starts the create connection sequence. Upon completion, there should exist an active
* connection through a connection service (or the call will have failed).
*
* @param phoneAccountRegistrar The phone account registrar.
*/
void startCreateConnection(PhoneAccountRegistrar phoneAccountRegistrar) {
Preconditions.checkState(mCreateConnectionProcessor == null);
mCreateConnectionProcessor = new CreateConnectionProcessor(this, mRepository, this,
phoneAccountRegistrar, mContext);
mCreateConnectionProcessor.process();
}
步骤17和18:继续把Call传递给private void attemptNextPhoneAccount() {
...
if (mResponse != null && attempt != null) {
Log.i(this, "Trying attempt %s", attempt);
ConnectionServiceWrapper service = mRepository.getService(
attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount.getComponentName());
if (service == null) {
Log.i(this, "Found no connection service for attempt %s", attempt);
attemptNextPhoneAccount();
} else {
mCall.setConnectionManagerPhoneAccount(attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount);
mCall.setTargetPhoneAccount(attempt.targetPhoneAccount);
mCall.setConnectionService(service);
Log.i(this, "Attempting to call from %s", service.getComponentName());
service.createConnection(mCall, new Response(service));
}
}
}
这样的话,Call对象就被传递到ConnectionServiceWrapper里了。
(读者最好先学习一下AIDL相关知识再继续阅读) 步骤20,21,22:这里调用了ConnectionServiceWrapper的父类ServiceBinder的bind()方法,先new一个ServiceConnection对象,然后绑定一个远程服务端服务。如果绑定成功的话,在ServiceBinder的内部类ServiceBinderConnection的onServiceConnected()方法就被调用。
在这里做了两件事:
1、步骤23和24:通过setBinder()方法,回调ConnectionServiceWrapper的setServiceInterface()方法,通过
mServiceInterface = IConnectionService.Stub.asInterface(binder); 这行代码获取一个远程服务端的对象mServiceInterface 。
2、步骤25和26:再通过调用handleSuccessfulConnection()方法回调callback 的onSuccess()方法,也就又回到ConnectionServiceWrapper的createConnection()方法里。
步骤27:最后通过这一行
mServiceInterface.createConnection(); ,调用
private final IBinder mBinder = new IConnectionService.Stub() {
...
@Override
public void createConnection(PhoneAccountHandle connectionManagerPhoneAccount,
String id,ConnectionRequest request,
boolean isIncoming,boolean isUnknown) {
SomeArgs args = SomeArgs.obtain();
args.arg1 = connectionManagerPhoneAccount;
args.arg2 = id;
args.arg3 = request;
args.argi1 = isIncoming ? 1 : 0;
args.argi2 = isUnknown ? 1 : 0;
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_CREATE_CONNECTION, args).sendToTarget();
}
...
}
步骤28:在这里把传进来的参数封装到Message里再发送出去,然后在private final Handler mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_CREATE_CONNECTION: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
try {
final PhoneAccountHandle connectionManagerPhoneAccount =
(PhoneAccountHandle) args.arg1;
final String id = (String) args.arg2;
final ConnectionRequest request = (ConnectionRequest) args.arg3;
final boolean isIncoming = args.argi1 == 1;
final boolean isUnknown = args.argi2 == 1;
if (!mAreAccountsInitialized) {
Log.d(this, "Enqueueing pre-init request %s", id);
mPreInitializationConnectionRequests.add(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
createConnection(connectionManagerPhoneAccount,
id,
request,
isIncoming,
isUnknown);
}
});
} else {
createConnection(connectionManagerPhoneAccount,
id,
request,
isIncoming,
isUnknown);
}
} finally {
args.recycle();
}
break;
}
...
}
步骤29,30,31:在这里就把Message里的数据取出来,然后传递到ConnectionService的createConnection()方法里。接着onCreateOutgoingConnection()会被调用到,这个方法被TelephonyConnectionService重写,TelephonyConnectionService是ConnectionService的实例,所以进入public Connection onCreateOutgoingConnection(
PhoneAccountHandle connectionManagerPhoneAccount,
final ConnectionRequest request) {
...
// 判断是不是紧急号码
boolean isEmergencyNumber = PhoneNumberUtils.isLocalEmergencyNumber(this, number);
// Get the right phone object from the account data passed in.
//创建phone 对象
final Phone phone = getPhoneForAccount(request.getAccountHandle(), isEmergencyNumber);
if (phone == null) {
Log.d(this, "onCreateOutgoingConnection, phone is null");
return Connection.createFailedConnection(
DisconnectCauseUtil.toTelecomDisconnectCause(
android.telephony.DisconnectCause.OUT_OF_SERVICE, "Phone is null"));
}
...
//创建connection对象
final TelephonyConnection connection =
createConnectionFor(phone, null, true /* isOutgoing */, null);
if (connection == null) {
return Connection.createFailedConnection(
DisconnectCauseUtil.toTelecomDisconnectCause(
android.telephony.DisconnectCause.OUTGOING_FAILURE,
"Invalid phone type"));
}
connection.setAddress(handle, PhoneConstants.PRESENTATION_ALLOWED);
connection.setInitializing();
connection.setVideoState(request.getVideoState());
if (useEmergencyCallHelper) {
if (mEmergencyCallHelper == null) {
mEmergencyCallHelper = new EmergencyCallHelper(this);
}
//打开Radio,关闭飞行模式
mEmergencyCallHelper.startTurnOnRadioSequence(phone,
new EmergencyCallHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public void onComplete(boolean isRadioReady) {
if (connection.getState() == Connection.STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
// If the connection has already been disconnected, do nothing.
} else if (isRadioReady) {
//Radio已被打开,可以拨打紧急电话
connection.setInitialized();
placeOutgoingConnection(connection, phone, request);
} else {
Log.d(this, "onCreateOutgoingConnection, failed to turn on radio");
connection.setDisconnected(
DisconnectCauseUtil.toTelecomDisconnectCause(
android.telephony.DisconnectCause.POWER_OFF,
"Failed to turn on radio."));
connection.destroy();
}
}
});
} else {
placeOutgoingConnection(connection, phone, request);
} return connection;
}
步骤32:在步骤30createConnection()方法的最后,调用了ConnectionServiceAdapter.java的handleCreateConnectionComplete()方法继续执行了一段流程,在创建Connection完成之后,会把Call的状态从CONNECTING更新为 DIALING。此段流程就不详说了。
步骤34~37:紧接着步骤33,最后通过phone.dial进行拨号,之后的流程就进入到Framework层了。 本文就写到这里。
如果想继续了解Framework层的流程,请看《Android 5.1 Phone MO(去电)流程分析(Framework层) 》