定义:对于正整数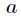 和
和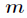 ,如果有
,如果有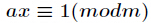 ,那么把这个同余方程中
,那么把这个同余方程中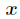 的最小正整数解叫做
的最小正整数解叫做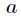 模
模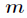 的逆元。
逆元一般用扩展欧几里得算法来求得,如果
的逆元。
逆元一般用扩展欧几里得算法来求得,如果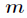 为素数,那么还可以根据费马小定理得到逆元为
为素数,那么还可以根据费马小定理得到逆元为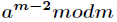 。
推导过程如下
。
推导过程如下
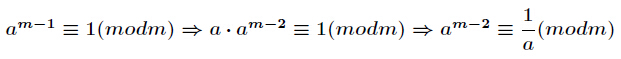 求现在来看一个逆元最常见问题,求如下表达式的值(已知
求现在来看一个逆元最常见问题,求如下表达式的值(已知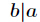 )
)
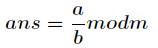 当然这个经典的问题有很多方法,最常见的就是扩展欧几里得,如果
当然这个经典的问题有很多方法,最常见的就是扩展欧几里得,如果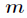 是素数,还可以用费马小定理。
但是你会发现费马小定理和扩展欧几里得算法求逆元是有局限性的,它们都会要求
是素数,还可以用费马小定理。
但是你会发现费马小定理和扩展欧几里得算法求逆元是有局限性的,它们都会要求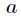 与
与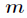 互素。实际上我们还有一
种通用的求逆元方法,适合所有情况。公式如下
互素。实际上我们还有一
种通用的求逆元方法,适合所有情况。公式如下
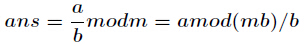 现在我们来证明它,已知
现在我们来证明它,已知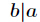 ,证明步骤如下
,证明步骤如下
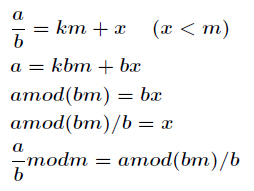 例题POJ1845 http://poj.org/problem?id=1845
题意:给定两个正整数
例题POJ1845 http://poj.org/problem?id=1845
题意:给定两个正整数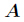 和
和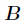 ,求
,求 的所有因子和对9901取余后的值。
分析:很容易知道,先把
的所有因子和对9901取余后的值。
分析:很容易知道,先把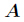 分解得到
分解得到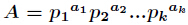 ,那么得到
,那么得到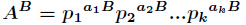 ,那么
,那么 的所有因子和的表达式如下
的所有因子和的表达式如下
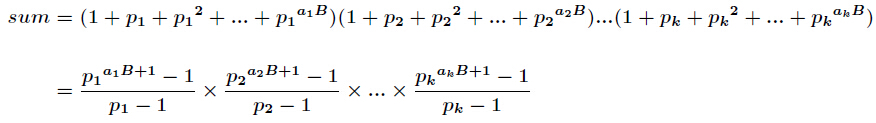
方法一:二分求等比数列和:
方法二:求逆元+等比数列求和公式
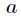 和
和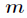 ,如果有
,如果有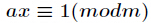 ,那么把这个同余方程中
,那么把这个同余方程中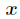 的最小正整数解叫做
的最小正整数解叫做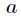 模
模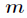 的逆元。
逆元一般用扩展欧几里得算法来求得,如果
的逆元。
逆元一般用扩展欧几里得算法来求得,如果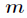 为素数,那么还可以根据费马小定理得到逆元为
为素数,那么还可以根据费马小定理得到逆元为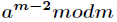 。
推导过程如下
。
推导过程如下
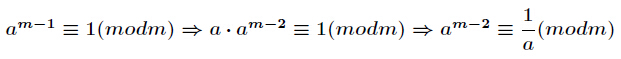 求现在来看一个逆元最常见问题,求如下表达式的值(已知
求现在来看一个逆元最常见问题,求如下表达式的值(已知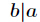 )
)
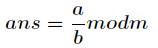 当然这个经典的问题有很多方法,最常见的就是扩展欧几里得,如果
当然这个经典的问题有很多方法,最常见的就是扩展欧几里得,如果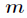 是素数,还可以用费马小定理。
但是你会发现费马小定理和扩展欧几里得算法求逆元是有局限性的,它们都会要求
是素数,还可以用费马小定理。
但是你会发现费马小定理和扩展欧几里得算法求逆元是有局限性的,它们都会要求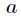 与
与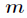 互素。实际上我们还有一
种通用的求逆元方法,适合所有情况。公式如下
互素。实际上我们还有一
种通用的求逆元方法,适合所有情况。公式如下
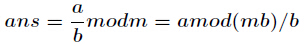 现在我们来证明它,已知
现在我们来证明它,已知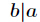 ,证明步骤如下
,证明步骤如下
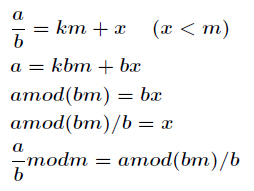 例题POJ1845 http://poj.org/problem?id=1845
题意:给定两个正整数
例题POJ1845 http://poj.org/problem?id=1845
题意:给定两个正整数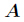 和
和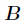 ,求
,求 的所有因子和对9901取余后的值。
分析:很容易知道,先把
的所有因子和对9901取余后的值。
分析:很容易知道,先把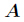 分解得到
分解得到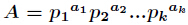 ,那么得到
,那么得到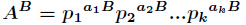 ,那么
,那么 的所有因子和的表达式如下
的所有因子和的表达式如下
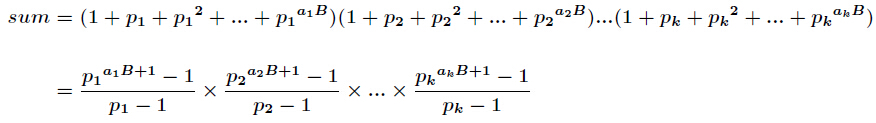
方法一:二分求等比数列和:
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#define debug
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MOD = 9901;
const int maxn = 10005;
int p[maxn],cnt;
int num[maxn];
bool prime[maxn];
void isprime()
{
cnt = 0;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(int i=2; i>=1;
a=a*a%MOD;
}
return ans;
}
LL sum(LL a,LL n)
{
if(n==0) return 1;
LL t=sum(a,(n-1)/2);
if(n&1){
LL tmp=quick_mod(a,(n+1)/2);
t=(t+t%MOD*tmp%MOD)%MOD;
}
else{
LL tmp=quick_mod(a,(n+1)/2);
t = (t + t % MOD * tmp % MOD) % MOD;
t = (t + quick_mod(a,n)) % MOD;
}
return t;
}
void solve(LL a,LL b)
{
//fenjie(a);
isprime();
LL ans=1;
#ifdef debug
cout<<"*****************"<1)
ans*=sum(a,b)%MOD;
printf("%lld
",ans%MOD);
}
int main()
{
LL a,b;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b)){
solve(a,b);
}
return 0;
}
方法二:求逆元+等比数列求和公式
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#define debug
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MOD = 9901;
const int maxn = 10005;
int p[maxn],cnt;
int num[maxn];
bool prime[maxn];
void isprime()
{
cnt = 0;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(int i=2; i>=1;
a=(a+a)%m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=1;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=multi(ans,a,m);
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=multi(a,a,m);
}
return ans;
}
void solve(LL a,LL b)
{
isprime();
LL ans=1;
for(int i=0;p[i]*p[i]<=a;i++){
if(a%p[i]==0){
int num=0;
while(a%p[i]==0)
num++,a/=p[i];
LL M = (p[i]-1)*MOD;
ans*=(quick_mod(p[i],num*b+1,M)+M-1)/(p[i]-1);
ans%=MOD;
}
}
if(a>1){
LL M=(a-1)*MOD;
ans*=(quick_mod(a,b+1,M)+M-1)/(a-1);
ans%=MOD;
}
printf("%lld
",ans);
}
int main()
{
LL a,b;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b)){
solve(a,b);
}
return 0;
}