######################### 字典的定义 #########################
"""
总结: 定义字典:
- 定义空字典, {}, dict()
- 赋值: d = {'key':'value', 'key1':'value1'}
- 初始化所有value值: fromkeys()
- 根据已有的数据创建字典:
users = ['user1', 'user2']
passwds = ['123', '456']
zip(users, passwds)
list(zip(users, passwds))
[('user1', '123'), ('user2', '456')]
userinfo = dict(zip(users, passwds))
userinfo
{'user1': '123', 'user2': '456'}

""" s = {}
print(type(s)) s = {
s = {
'fentiao':[100, 80, 90],
'westos':[100,100,100]
}
print(s, type(s)) d = dict()
d = dict()
print(d, type(d))
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d, type(d))
cardinfo = {
'001':'000000',
'002':'000000',
} # 随机生成100张卡号, 卡号的格式为610 334455 001 ---610 334455 100 cards = [ ]
for cardId in range(100):
card = "610 334455 %.3d" %(cardId+1)
cards.append(card)
print(cards) #
print({}.fromkeys(cards))
print({}.fromkeys(cards, '666666')) """
# 定义空集合, 必须set(),
"""
# 定义空集合, 必须set(),
# {}默认的类型为字典;
d = {}
print(type(d)) # 字典: key-value值, 键值对;
# value值可以是任意数据类型: int,float,long, complex, list, tuple,set, dict
d = {
'王旭': [18, '男', "请假"],
'张龙': [18, '男', '俯卧撑']
} print(d['张龙']) d2 = {
'a': 1,
'b': 2
} print(d2) d3 = {
'a': {1, 2, 3},
'b': {2, 3, 4}
}
print(d3) # 字典的嵌套;
students = {
'13021001': {
'name':'张龙',
'age':18,
'score':100
},
'13021003': {
'name': '张',
'age': 18,
'score': 90
}
}
print(students['13021003']['name']) # 工厂函数;
l = list([1,2,3])
print(l) d5 = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d5) # cardinfo = {
'001':'000000',
'002':'000000'
}
# fromkeys第一个参数可以列表/tuple/str/set, 将列表的每一个元素作为字典的key值,
# 并且所有key的value值一致, 都为'000000';
print({}.fromkeys({'1', '2'}, '000000'))
# 字典必须是不可变数据类型;d = {[1,2,3]:1}(x) # 可变数据类型:list, set, dict
# 可变数据类型:list, set, dict
# 不可变: 数值类型, str, tuple """ ########################### 字典的特性 ################################# # (索引, 切片, 重复, 连接,)X 成员操作符 √ d = dict(a=1, b=2) print(d)
# print(d[0])
# print(d[1:])
# print(d+d)
# print(d*3) # 成员操作符, 默认判断key值是否存在.
print('a' in d)
print(1 in d)
# for循环: 默认遍历字典的key值;
for i in d:
print(i)
for i,v in enumerate(d):
print(i, '-----', v) ############################### 字典的增加 ##############################
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
# 添加或者更改key-value对
############################### 字典的增加 ##############################
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
# 添加或者更改key-value对
d['g'] = 10
d['a'] = 10
print(d) # # update:
# # update:
# # 如果key值已经存在, 更新value值;
# # 如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;
# d.update({'a':4, 'f':1})
# print(d)

#
# # setdefault
# # # 如果key值已经存在, 不做修改;
# # 如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;默认情况下value值为None
# d.setdefault('g', 10)
# print(d) ############################## 字典的删除 ############################ d = dict(a=1, b=2, c=3) # pop:弹出指定key-value值
# d.pop('a')
# print(d)
# popitem
# d.popitem()
# print(d)
# del d['a']
# print(d) d.clear()
d.clear()
print(d) ################################ 字典的修改与查看 #######################
services = {
################################ 字典的修改与查看 #######################
services = {
'http':80,
'mysql':3306
}
# 查看字典里面所有的key值
print(services.keys()) # 查看字典里面所有的value值
# 查看字典里面所有的value值
print(services.values())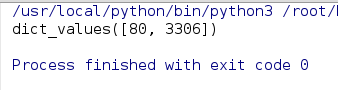 # 查看字典里面所有的key-value值
# 查看字典里面所有的key-value值
print(services.items()) # 遍历
# 遍历
for k,v in services.items(): # k,v = ('http', 80)
print(k , '--->', v) for k in services:
print(k, '--->', services[k])
# 查看指定key对应的value值, 注意: key不存在, 就会报错
print(services['http'])
# print(services['https']) #
# if 'https' in services:
# print(services['https'])
# else:
# print('key not exist')
# get方法获取指定可以对应的value值
# 如果key值存在, 返回对应的value值;
# 如果key值不存在, 默认返回None, 如果需要指定返回的值, 传值即可;
print(services.get('https', 'key not exist'))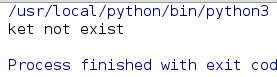 ############################ 通过字典实现switch语句 #######################
# python里面不支持switch语句;
############################ 通过字典实现switch语句 #######################
# python里面不支持switch语句;
# C/C++/Java/Javascript:switch语句是用来简化if语句的.
grade = 'B'
if grade == 'A':
print("优秀")
elif grade == 'B':
print("良好")
elif grade == 'C':
print("合格")
else:
print('无效的成绩') """
C++:
char grade = 'B' switch(grade)
{
case 'A':
print('')
break
case 'B':
print('')
break
default:
print('error')
}
"""
grade = 'D'
d = {
'A': '优秀',
'B':'良好',
'C':"及格"
}
# if grade in d:
# print(d[grade])
# else:
# print("无效的成绩") print(d.get(grade, "无效的成绩")) ############################# 字典练习 ################################### """
# 重复的单词: 此处认为单词之间以空格为分隔符, 并且不包含,和.;
# 1. 用户输入一句英文句子;
# 2. 打印出每个单词及其重复的次数; s = input("s:") # "hello java hello python"
# hello 3
# java 2
# python 1
# 1. 把每个单词分割处理;
s_li = s.split()
print(s_li)
# 2. 通过字典存储单词和该单词出现的次数;
words_dict = {}
# 3. # 依次循环遍历列表,
如果列表元素不在字典的key中,将元素作为key, 1作为value加入字典;
如果列表元素在字典的key中,直接更新value值, 即在原有基础上加1
li = ['hello', 'java', 'hello', 'python']
words_dict = {'hello':2,'java':1 } for item in s_li:
if item not in words_dict:
words_dict[item] = 1
else:
# words_dict[item] = words_dict[item] + 1
words_dict[item] += 1 # 4. 打印生成的字典;
print(words_dict)
""" # ********************* 简易方法实现**********************
from collections import defaultdict
from collections import Counter
# **************1.统计每个单词出现的次数************
# s = input('s:') # 'a b a c'
s = 'a b b b c f g w e b a c c d'
li = s.split() # ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
wordDict = defaultdict(int)
for word in li:
wordDict[word] += 1
print(wordDict.items()) # *******************2. 找出单词出现次数最多的3个单词**********
c = Counter(wordDict)
print(c.most_common(5))
 """
** 需求:
"""
** 需求:
假设已有若干用户名字及其喜欢的电影清单,
现有某用户, 已看过并喜欢一些电影, 现在想找
新电影看看, 又不知道看什么好.
** 思路:
根据已有数据, 查找与该用户爱好最相似的用户,
即看过并喜欢的电影与该用户最接近,
然后从那个用户喜欢的电影中选取一个当前用户还没看过的电影进行推荐.
""" # 1. 随机生成电影清单
import random
data = {}
for userItem in range(10):
files = set([])
for fileItem in range(random.randint(4,15)):
files.add( "film" + str(fileItem))
data["user"+str(userItem)] = files
print(data)
总结: 定义字典:
- 定义空字典, {}, dict()
- 赋值: d = {'key':'value', 'key1':'value1'}
- 初始化所有value值: fromkeys()
- 根据已有的数据创建字典:
users = ['user1', 'user2']
passwds = ['123', '456']
zip(users, passwds)
list(zip(users, passwds))
[('user1', '123'), ('user2', '456')]
userinfo = dict(zip(users, passwds))
userinfo
{'user1': '123', 'user2': '456'}


""" s = {}
print(type(s))
 s = {
s = {'fentiao':[100, 80, 90],
'westos':[100,100,100]
}
print(s, type(s))
 d = dict()
d = dict()print(d, type(d))

d = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d, type(d))

cardinfo = {
'001':'000000',
'002':'000000',
} # 随机生成100张卡号, 卡号的格式为610 334455 001 ---610 334455 100 cards = [ ]
for cardId in range(100):
card = "610 334455 %.3d" %(cardId+1)
cards.append(card)
print(cards) #
print({}.fromkeys(cards))
print({}.fromkeys(cards, '666666'))
 """
# 定义空集合, 必须set(),
"""
# 定义空集合, 必须set(),# {}默认的类型为字典;
d = {}
print(type(d)) # 字典: key-value值, 键值对;
# value值可以是任意数据类型: int,float,long, complex, list, tuple,set, dict
d = {
'王旭': [18, '男', "请假"],
'张龙': [18, '男', '俯卧撑']
} print(d['张龙']) d2 = {
'a': 1,
'b': 2
} print(d2) d3 = {
'a': {1, 2, 3},
'b': {2, 3, 4}
}
print(d3) # 字典的嵌套;
students = {
'13021001': {
'name':'张龙',
'age':18,
'score':100
},
'13021003': {
'name': '张',
'age': 18,
'score': 90
}
}
print(students['13021003']['name']) # 工厂函数;
l = list([1,2,3])
print(l) d5 = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d5) # cardinfo = {
'001':'000000',
'002':'000000'
}
# fromkeys第一个参数可以列表/tuple/str/set, 将列表的每一个元素作为字典的key值,
# 并且所有key的value值一致, 都为'000000';
print({}.fromkeys({'1', '2'}, '000000'))
# 字典必须是不可变数据类型;d = {[1,2,3]:1}(x)
 # 可变数据类型:list, set, dict
# 可变数据类型:list, set, dict# 不可变: 数值类型, str, tuple """ ########################### 字典的特性 ################################# # (索引, 切片, 重复, 连接,)X 成员操作符 √ d = dict(a=1, b=2) print(d)
# print(d[0])
# print(d[1:])
# print(d+d)
# print(d*3) # 成员操作符, 默认判断key值是否存在.
print('a' in d)
print(1 in d)

# for循环: 默认遍历字典的key值;
for i in d:
print(i)

for i,v in enumerate(d):
print(i, '-----', v)
 ############################### 字典的增加 ##############################
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
# 添加或者更改key-value对
############################### 字典的增加 ##############################
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
# 添加或者更改key-value对d['g'] = 10
d['a'] = 10
print(d)
 # # update:
# # update:# # 如果key值已经存在, 更新value值;
# # 如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;
# d.update({'a':4, 'f':1})
# print(d)

#
# # setdefault
# # # 如果key值已经存在, 不做修改;
# # 如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;默认情况下value值为None
# d.setdefault('g', 10)
# print(d) ############################## 字典的删除 ############################ d = dict(a=1, b=2, c=3) # pop:弹出指定key-value值
# d.pop('a')
# print(d)

# popitem
# d.popitem()
# print(d)

# del d['a']
# print(d)
 d.clear()
d.clear()print(d)
 ################################ 字典的修改与查看 #######################
services = {
################################ 字典的修改与查看 #######################
services = {'http':80,
'mysql':3306
}
# 查看字典里面所有的key值
print(services.keys())
 # 查看字典里面所有的value值
# 查看字典里面所有的value值print(services.values())
 # 查看字典里面所有的key-value值
# 查看字典里面所有的key-value值print(services.items())
 # 遍历
# 遍历for k,v in services.items(): # k,v = ('http', 80)
print(k , '--->', v) for k in services:
print(k, '--->', services[k])

# 查看指定key对应的value值, 注意: key不存在, 就会报错
print(services['http'])

# print(services['https']) #
# if 'https' in services:
# print(services['https'])
# else:
# print('key not exist')
# get方法获取指定可以对应的value值
# 如果key值存在, 返回对应的value值;
# 如果key值不存在, 默认返回None, 如果需要指定返回的值, 传值即可;
print(services.get('https', 'key not exist'))
 ############################ 通过字典实现switch语句 #######################
# python里面不支持switch语句;
############################ 通过字典实现switch语句 #######################
# python里面不支持switch语句;# C/C++/Java/Javascript:switch语句是用来简化if语句的.
grade = 'B'
if grade == 'A':
print("优秀")
elif grade == 'B':
print("良好")
elif grade == 'C':
print("合格")
else:
print('无效的成绩') """
C++:
char grade = 'B' switch(grade)
{
case 'A':
print('')
break
case 'B':
print('')
break
default:
print('error')
}
"""
grade = 'D'
d = {
'A': '优秀',
'B':'良好',
'C':"及格"
}
# if grade in d:
# print(d[grade])
# else:
# print("无效的成绩") print(d.get(grade, "无效的成绩")) ############################# 字典练习 ################################### """
# 重复的单词: 此处认为单词之间以空格为分隔符, 并且不包含,和.;
# 1. 用户输入一句英文句子;
# 2. 打印出每个单词及其重复的次数; s = input("s:") # "hello java hello python"
# hello 3
# java 2
# python 1
# 1. 把每个单词分割处理;
s_li = s.split()
print(s_li)
# 2. 通过字典存储单词和该单词出现的次数;
words_dict = {}
# 3. # 依次循环遍历列表,
如果列表元素不在字典的key中,将元素作为key, 1作为value加入字典;
如果列表元素在字典的key中,直接更新value值, 即在原有基础上加1
li = ['hello', 'java', 'hello', 'python']
words_dict = {'hello':2,'java':1 } for item in s_li:
if item not in words_dict:
words_dict[item] = 1
else:
# words_dict[item] = words_dict[item] + 1
words_dict[item] += 1 # 4. 打印生成的字典;
print(words_dict)
""" # ********************* 简易方法实现**********************
from collections import defaultdict
from collections import Counter
# **************1.统计每个单词出现的次数************
# s = input('s:') # 'a b a c'
s = 'a b b b c f g w e b a c c d'
li = s.split() # ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
wordDict = defaultdict(int)
for word in li:
wordDict[word] += 1
print(wordDict.items()) # *******************2. 找出单词出现次数最多的3个单词**********
c = Counter(wordDict)
print(c.most_common(5))

 """
** 需求:
"""
** 需求:假设已有若干用户名字及其喜欢的电影清单,
现有某用户, 已看过并喜欢一些电影, 现在想找
新电影看看, 又不知道看什么好.
** 思路:
根据已有数据, 查找与该用户爱好最相似的用户,
即看过并喜欢的电影与该用户最接近,
然后从那个用户喜欢的电影中选取一个当前用户还没看过的电影进行推荐.
""" # 1. 随机生成电影清单
import random
data = {}
for userItem in range(10):
files = set([])
for fileItem in range(random.randint(4,15)):
files.add( "film" + str(fileItem))
data["user"+str(userItem)] = files
print(data)