原文http://blog.csdn.net/jinshengtao/article/details/26278725
前些日子一直在忙答辩的事情,毕业后去了华为,图像处理什么的都派不上用场了。打算分3-4篇文章,把我研究生阶段学过的常用算法为大家和4107的师弟师妹们分享下。本次介绍混合高斯背景建模算法,还是老样子,首先介绍理论部分,然后给出代码,最后实验贴图。
一、理论
混合高斯背景建模是基于像素样本统计信息的背景表示方法,利用像素在较长时间内大量样本值的概率密度等统计信息(如模式数量、每个模式的均值和标准差)表示背景,然后使用统计差分(如3σ原则)进行目标像素判断,可以对复杂动态背景进行建模,计算量较大。
在混合高斯背景模型中,认为像素之间的颜 {MOD}信息互不相关,对各像素点的处理都是相互独立的。对于视频图像中的每一个像素点,其值在序列图像中的变化可看作是不断产生像素值的随机过程,即用高斯分布来描述每个像素点的颜 {MOD}呈现规律【单模态(单峰),多模态(多峰)】。
对于多峰高斯分布模型,图像的每一个像素点按不同权值的多个高斯分布的叠加来建模,每种高斯分布对应一个可能产生像素点所呈现颜 {MOD}的状态,各个高斯分布的权值和分布参数随时间更新。当处理彩 {MOD}图像时,假定图像像素点R、G、B三 {MOD}通道相互独立并具有相同的方差。对于随机变量X的观测数据集{x1,x2,…,xN},xt=(rt,gt,bt)为t时刻像素的样本,则单个采样点xt其服从的混合高斯分布概率密度函数:
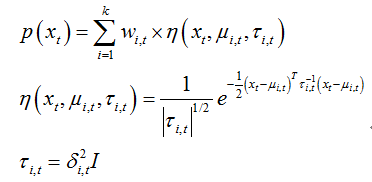
其中k为分布模式总数,η(xt,μi,t, τi,t)为t时刻第i个高斯分布,μi,t为其均值,τi,t为其协方差矩阵,δi,t为方差,I为三维单位矩阵,ωi,t为t时刻第i个高斯分布的权重。 详细算法流程:

二、代码实现
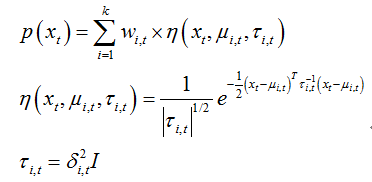
其中k为分布模式总数,η(xt,μi,t, τi,t)为t时刻第i个高斯分布,μi,t为其均值,τi,t为其协方差矩阵,δi,t为方差,I为三维单位矩阵,ωi,t为t时刻第i个高斯分布的权重。 详细算法流程:


二、代码实现
// my_mixgaussians.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
CvCapture *capture=cvCreateFileCapture("test.avi");
IplImage *mframe,*current,*frg,*test;
int *fg,*bg_bw,*rank_ind;
double *w,*mean,*sd,*u_diff,*rank;
int C,M,sd_init,i,j,k,m,rand_temp=0,rank_ind_temp=0,min_index=0,x=0,y=0,counter_frame=0;
double D,alph,thresh,p,temp;
CvRNG state;
int match,height,width;
mframe=cvQueryFrame(capture);
frg = cvCreateImage(cvSize(mframe->width,mframe->height),IPL_DEPTH_8U,1);
current = cvCreateImage(cvSize(mframe->width,mframe->height),IPL_DEPTH_8U,1);
test = cvCreateImage(cvSize(mframe->width,mframe->height),IPL_DEPTH_8U,1);
C = 4; //number of gaussian components (typically 3-5)
M = 4; //number of background components
sd_init = 6; //initial standard deviation (for new components) var = 36 in paper
alph = 0.01; //learning rate (between 0 and 1) (from paper 0.01)
D = 2.5; //positive deviation threshold
thresh = 0.25; //foreground threshold (0.25 or 0.75 in paper)
p = alph/(1/C); //initial p variable (used to update mean and sd)
height=current->height;width=current->widthStep;
fg = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*width*height); //foreground array
bg_bw = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*width*height); //background array
rank = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*1*C); //rank of components (w/sd)
w = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*width*height*C); //weights array
mean = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*width*height*C); //pixel means
sd = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*width*height*C); //pixel standard deviations
u_diff = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*width*height*C); //difference of each pixel from mean
for (i=0;iimageData[i*width+j]-mean[i*width*C+j*C+m]);
}
}
}
//update gaussian components for each pixel
for (i=0;iimageData[i*width+j];
sd[i*width*C+j*C+k] =sqrt((1-p)*(sd[i*width*C+j*C+k]*sd[i*width*C+j*C+k]) + p*(pow((uchar)current->imageData[i*width+j] - mean[i*width*C+j*C+k],2)));
}else{
w[i*width*C+j*C+k] = (1-alph)*w[i*width*C+j*C+k]; // weight slighly decreases
}
temp += w[i*width*C+j*C+k];
}
for(k=0;kimageData[i*width+j] = (uchar)bg_bw[i*width+j];
//if no components match, create new component
if (match == 0)
{
mean[i*width*C+j*C+min_index] = (uchar)current->imageData[i*width+j];
//printf("%d ",(uchar)bg->imageData[i*width+j]);
sd[i*width*C+j*C+min_index] = sd_init;
}
for (k=0;k rank[m])
{
//swap max values
rand_temp = rank[m];
rank[m] = rank[k];
rank[k] = rand_temp;
//swap max index values
rank_ind_temp = rank_ind[m];
rank_ind[m] = rank_ind[k];
rank_ind[k] = rank_ind_temp;
}
}
}
//calculate foreground
match = 0;k = 0;
//frg->imageData[i*width+j]=0;
while ((match == 0)&&(k= thresh)
if (abs(u_diff[i*width*C+j*C+rank_ind[k]]) <= D*sd[i*width*C+j*C+rank_ind[k]]){
frg->imageData[i*width+j] = 0;
match = 1;
}
else
frg->imageData[i*width+j] = (uchar)current->imageData[i*width+j];
k = k+1;
}
}
}
mframe = cvQueryFrame(capture);
cvShowImage("fore",frg);
cvShowImage("back",test);
char s=cvWaitKey(33);
if(s==27) break;
free(rank_ind);
}
free(fg);free(w);free(mean);free(sd);free(u_diff);free(rank);
cvNamedWindow("back",0);
cvNamedWindow("fore",0);
cvReleaseCapture(&capture);
cvDestroyWindow("fore");
cvDestroyWindow("back");
return 0;
}