题目连接:http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/A
A. One-dimensional Japanese Crossword time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standard output Recently Adaltik discovered japanese crosswords. Japanese crossword is a picture, represented as a table sized a × b squares, and each square is colored white or black. There are integers to the left of the rows and to the top of the columns, encrypting the corresponding row or column. The number of integers represents how many groups of black squares there are in corresponding row or column, and the integers themselves represents the number of consecutive black squares in corresponding group (you can find more detailed explanation in Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_crossword). Adaltik decided that the general case of japanese crossword is too complicated and drew a row consisting of n squares (e.g. japanese crossword sized 1 × n), which he wants to encrypt in the same way as in japanese crossword.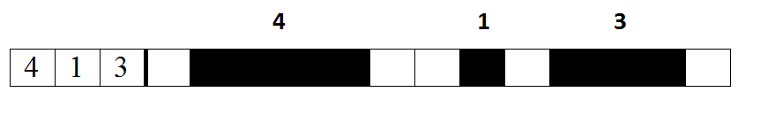 The
example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.
The
example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.
题目大意:找多少段连续的‘B’。
解题思路:直接模拟。
A. One-dimensional Japanese Crossword time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standard output Recently Adaltik discovered japanese crosswords. Japanese crossword is a picture, represented as a table sized a × b squares, and each square is colored white or black. There are integers to the left of the rows and to the top of the columns, encrypting the corresponding row or column. The number of integers represents how many groups of black squares there are in corresponding row or column, and the integers themselves represents the number of consecutive black squares in corresponding group (you can find more detailed explanation in Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_crossword). Adaltik decided that the general case of japanese crossword is too complicated and drew a row consisting of n squares (e.g. japanese crossword sized 1 × n), which he wants to encrypt in the same way as in japanese crossword.
 The
example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.
The
example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.题目大意:找多少段连续的‘B’。
解题思路:直接模拟。
/* ***********************************************
┆ ┏┓ ┏┓ ┆
┆┏┛┻━━━┛┻┓ ┆
┆┃ ┃ ┆
┆┃ ━ ┃ ┆
┆┃ ┳┛ ┗┳ ┃ ┆
┆┃ ┃ ┆
┆┃ ┻ ┃ ┆
┆┗━┓ 马 ┏━┛ ┆
┆ ┃ 勒 ┃ ┆
┆ ┃ 戈 ┗━━━┓ ┆
┆ ┃ 壁 ┣┓┆
┆ ┃ 的草泥马 ┏┛┆
┆ ┗┓┓┏━┳┓┏┛ ┆
┆ ┃┫┫ ┃┫┫ ┆
┆ ┗┻┛ ┗┻┛ ┆
************************************************ */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include