声明:本文是看韦东山老师的视频并看过一些文章后总结的关于nor的驱动,如果您觉得我的文章已经对你有所侵犯,请联系我,我会对我的文章进行更改或删除。如果对您有帮助,那是我的荣幸。
下面我们言归正传,开始讲nor flash驱动。我想我们在开始写驱动之前都会参考他人的驱动来写,我们也不例外。我们参考的是内核自带的nor驱动:drivers/mtd/maps/physmap.c。通过分析physmap.c我们总结写驱动所需要的步骤并按着这个步骤写一个更加简练的驱动程序。
下面我们还是以上一篇文章所介绍的图开始:
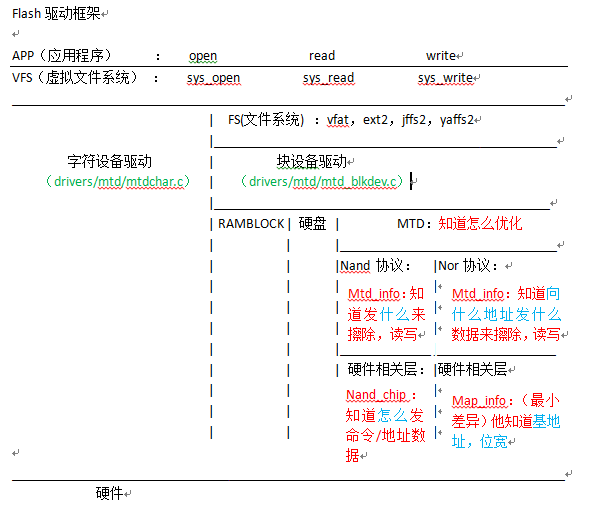 上一篇文章我已经对这个图做了介绍,现在就不介绍了,而是想通过这幅图来引出对physmap.c的分析。我们从图中知道nor协议层已经写好,并且通过mtd_info结构体可以知道向什么地址发什么数据来擦除,读写。而我们要做的就是在硬件相关层来对map_info结构体进行填充基地址和位宽这些有差异的东西。并通过map_info来匹配合适的mtd_info。
有了上面的分析,我们解析physmap.c也会更方便一些。下面我们开始分析physmap.c。同样我们先从入口函数开始分析:
上一篇文章我已经对这个图做了介绍,现在就不介绍了,而是想通过这幅图来引出对physmap.c的分析。我们从图中知道nor协议层已经写好,并且通过mtd_info结构体可以知道向什么地址发什么数据来擦除,读写。而我们要做的就是在硬件相关层来对map_info结构体进行填充基地址和位宽这些有差异的东西。并通过map_info来匹配合适的mtd_info。
有了上面的分析,我们解析physmap.c也会更方便一些。下面我们开始分析physmap.c。同样我们先从入口函数开始分析:
1. make menuconfig
-> Device Drivers
-> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support
-> Mapping drivers for chip access
CFI Flash device in physical memory map
(0x0) Physical start address of flash mapping /* 物理基地址 */
(0x1000000) Physical length of flash mapping /* 长度 */
(2) Bank width in octets (NEW) /* 位宽 */
2. make modules /* 生成模块 */
cp drivers/mtd/maps/physmap.ko /work/nfs_root/first_fs /* 将模块拷入文件系统 */
3. 启动开发板
ls /dev/mtd* /* 查询是否有mtd设备 */
insmod physmap.ko /* 安装模块 */
ls /dev/mtd* /* 再次查询是否有mtd设备 */
cat /proc/mtd /* 再次查询是否有mtd设备 */ 下面是我根据上面步骤写的nor驱动:
static int __init physmap_init(void)
{
int err;
err = platform_driver_register(&physmap_flash_driver); /* 平台驱动注册 */
#ifdef PHYSMAP_COMPAT
if (err == 0)
platform_device_register(&physmap_flash); /* 平台设备注册 */
#endif
return err;
}
我们会发现这个入口函数中既有平台设备的注册,又有平台驱动的注册。这其实对我们分析代码来说还是有好处的,因为有时候我们只有平台驱动的注册而没有平台设备的注册,而当我们需要平台设备的信息时却要找好久才能找到,而现在平台设备的信息就在这里,我们可以很方便的获得设备的信息。所以我们先看一下注册的平台设备,了解一下设备信息:
static struct platform_device physmap_flash = {
.name = "physmap-flash", /* 姓名 */
.id = 0,
.dev = { /* 设备信息 */
.platform_data = &physmap_flash_data,
},
.num_resources = 1, /* 有几个资源 */
.resource = &physmap_flash_resource, /* 详细的资源信息 */
};
我们知道平台设备驱动中,设备和驱动所匹配的就是姓名,所以第一项为姓名。而比较重要的是设备信息和资源信息,我们先看设备信息,设备信息主要定义了位宽:
static struct physmap_flash_data physmap_flash_data = {
.width = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_BANKWIDTH, /* 位宽为:16bit */
};
然后是资源信息,资源信息主要是物理基地址和地址结束:
static struct resource physmap_flash_resource = {
.start = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START,
.end = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START + CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN - 1,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
};
而上面主要的三个变量:CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_BANKWIDTH(nor flash的字节位宽),CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START(nor flash的物理基地址),CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN(nor flash的容量长度)是通过linux的menuconfig菜单配置出来的,若自己填入值,就不需要用menuconfig菜单配置了
看完注册设备,接下来我们看注册驱动,同样我们直接进入probe函数,同时为了方便分析,我会将一些判断语句删除以使得代码看上去更简洁:
static int physmap_flash_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct physmap_flash_data *physmap_data; /* 该结构体中包含了设备有关的信息 */
struct physmap_flash_info *info; /* 该结构体中包含了map_info结构体和mtd_info结构体 */
const char **probe_type;
int err;
physmap_data = dev->dev.platform_data;
info = kzalloc(sizeof(struct physmap_flash_info), GFP_KERNEL); /* 为info分配空间 */
platform_set_drvdata(dev, info);
info->res = request_mem_region(dev->resource->start,
dev->resource->end - dev->resource->start + 1,
dev->dev.bus_id);
/* 设置map_info结构体 */
info->map.name = dev->dev.bus_id; /* nor 的名字 */
info->map.phys = dev->resource->start; /* 物理基地址 */
info->map.size = dev->resource->end - dev->resource->start + 1; /* 大小 */
info->map.bankwidth = physmap_data->width; /* 位宽 */
info->map.set_vpp = physmap_data->set_vpp;
info->map.virt = ioremap(info->map.phys, info->map.size); /* 虚拟基地址 ,通过物理基地址重映射得到*/
simple_map_init(&info->map); /* 简单的初始化 */
/* 设置mtd_info结构体 */
probe_type = rom_probe_types; /* probe的类型有CFI和jedec两种规格 */
for (; info->mtd == NULL && *probe_type != NULL; probe_type++)
info->mtd = do_map_probe(*probe_type, &info->map); /* nor探测,如果有匹配的nor芯片则返回该芯片的mtd_info结构体 */
info->mtd->owner = THIS_MODULE; /* 设置owner为THIS_MODULE */
if (physmap_data->nr_parts) { /* 如果有分区信息,对nor进行分区 */
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Using physmap partition information
");
add_mtd_partitions(info->mtd, physmap_data->parts,physmap_data->nr_parts); /* 添加分区,并创建各分区的字符设备和块设备 */
return 0;
}
add_mtd_device(info->mtd); /* 如果没有分区信息,则创建整体的字符设备和块设备 */
通过上面的分析我们知道通过rom_probe_types来选择我们使用CFI还是jedec。
static const char *rom_probe_types[] = { "cfi_probe", "jedec_probe", "map_rom", NULL };
而选择不同的规格,将会在do_map_probe中走不一样的路径。例如:当我们选CFI,程序会通过do_map_probe自己识别芯片的尺寸,位宽等信息。而当你选jedec,程序会读出厂家ID设备ID后去与jedec_table[]数组进行匹配。
通过上面的分析我们可以总结出写nor驱动的步骤:
1.分配一个map_info结构体
2.设置map_info结构体,如物理基地址(phys),大小(size),位宽(bankwidth),物理基地址(virt)
3.使用do_map_probe调用nor协议层提供的函数来识别
4.添加分区add_mtd_partitions或者添加设备add_mtd_device,来创建字符设备和块设备
在写自己的驱动程序之前我想先将内核提供的驱动信息加载到内核:
配置内核支持NOR FLASH 1. make menuconfig
-> Device Drivers
-> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support
-> Mapping drivers for chip access
(0x0) Physical start address of flash mapping /* 物理基地址 */
(0x1000000) Physical length of flash mapping /* 长度 */
(2) Bank width in octets (NEW) /* 位宽 */
2. make modules /* 生成模块 */
cp drivers/mtd/maps/physmap.ko /work/nfs_root/first_fs /* 将模块拷入文件系统 */
3. 启动开发板
ls /dev/mtd* /* 查询是否有mtd设备 */
insmod physmap.ko /* 安装模块 */
ls /dev/mtd* /* 再次查询是否有mtd设备 */
cat /proc/mtd /* 再次查询是否有mtd设备 */ 下面是我根据上面步骤写的nor驱动:
/*
*可以参考driversmtdmapsphysmap.c
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static struct map_info *s3c_nor_map;
static struct mtd_info *s3c_nor_mtd;
static struct mtd_partition s3c_nor_parts[] = {
[0] = {
.name = "bootloader_nor",
.size = 0x00040000,
.offset = 0,
},
[1] = {
.name = "root_nor",
.size = MTDPART_SIZ_FULL,
.offset = MTDPART_OFS_APPEND,
}
};
static int s3c_nor_init(void)
{
/* 1. 分配一个map_info结构体 */
s3c_nor_map = kzalloc(sizeof(struct map_info),GFP_KERNEL);
/* 2. 设置map_info结构体,物理基地址(phys),大小(size),位宽(bankwidth),虚拟基地址(virt)*/
s3c_nor_map->name = "s3c_nor";
s3c_nor_map->phys = 0;
s3c_nor_map->size = 0x1000000; /* 这个参数一定要大于等于Nor Flash的真正大小 */
s3c_nor_map->bankwidth = 2 ; /* 2表示2*8 =16,本设备的位宽为16位 */
s3c_nor_map->virt = ioremap(s3c_nor_map->phys,s3c_nor_map->size);
simple_map_init(s3c_nor_map);
/* 3. 使用,调用nor flash协议层提供的函数:do_map_probe来识别 */
printk("use cfi_probe
");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("cfi_probe", s3c_nor_map);
if(!s3c_nor_mtd){
printk(" use jedec_probe
");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("jedec_probe", s3c_nor_map);
}
if(!s3c_nor_mtd){
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
return -EIO;
}
s3c_nor_mtd->owner = THIS_MODULE;
/* 4. 添加分区:add_mtd_partitions */
add_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd, s3c_nor_parts, 2);
return 0;
}
static void s3c_nor_exit(void)
{
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
del_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd);
}
module_init(s3c_nor_init);
module_exit(s3c_nor_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
最后分享几个关于nor的博客,我有一些东西也是借鉴他们的:
25.Linux-Nor Flash驱动(详解)