❤ 2019.3.6
今天开始学习DSP,over。
我用的版本是德州仪器的TMS320F28335,用的开发板是研旭的TMS320F28335至尊开发板,到底有多至尊我也不知道,不过看起来教材和资料挺全的。


 〇 基础知识
● DSP的历史
略(自己看书百度去)
● 数字信号处理特点
〇 基础知识
● DSP的历史
略(自己看书百度去)
● 数字信号处理特点
 ● DSP主要特点
● DSP主要特点
 ● TI的芯片系列
● TI的芯片系列
 F28335系列属于C2000系列,在TI看来不属于DSP,属于MCU,但是我们就当成DSP学(?)
● C2000系列简介
F28335系列属于C2000系列,在TI看来不属于DSP,属于MCU,但是我们就当成DSP学(?)
● C2000系列简介
 ● DSP系统开发
● DSP系统开发
 ● 如何成为一个优秀的DSP工程师
● 如何成为一个优秀的DSP工程师
 (真的假的?)
● 教程总纲
(真的假的?)
● 教程总纲
 〇 DSP开发环境介绍
● CCS介绍
〇 DSP开发环境介绍
● CCS介绍
 ● CCS安装
(略)
● 仿真器
○ CCS6如何连接仿真器(这个手册上面有)
1、建立target configuration file
● CCS安装
(略)
● 仿真器
○ CCS6如何连接仿真器(这个手册上面有)
1、建立target configuration file
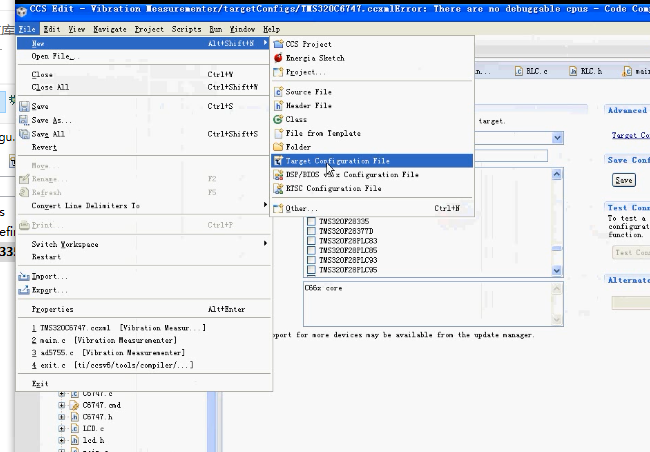 2、输入名字
2、输入名字
 3、选择仿真器、芯片,然后点save
3、选择仿真器、芯片,然后点save
 ♣ 经常会在工程文件里生成一个target configuration 文件
♣ 经常会在工程文件里生成一个target configuration 文件
 ❤ 2019.3.22
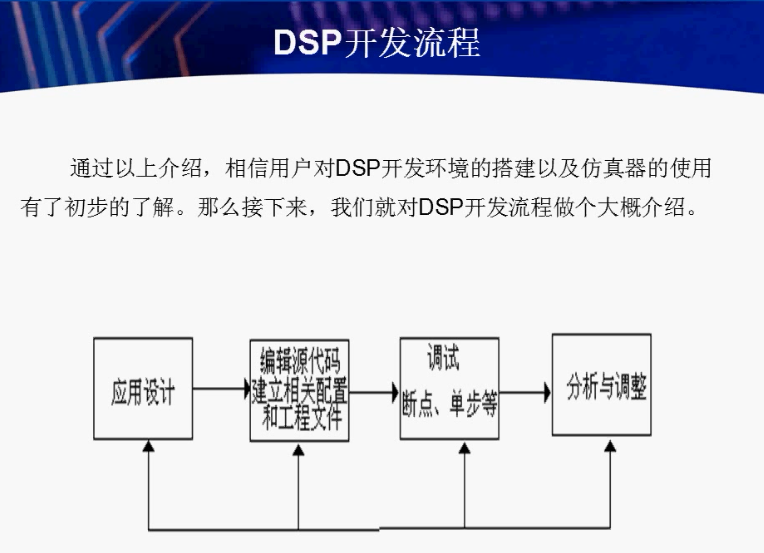
〇 DSP开发流程
❤ 2019.3.22
〇 DSP开发流程
 ○ CMD文件(配置文件)
指定DSP内部的硬件存储器的一些相关地址以及长度。
包含两部分:MEMORY以及SECTIONS
MEMORY:指定DSP内部的ram和flash的首地址以及长度
SECTIONS:指定程序组成部分对应内存的储存部分(MEMORY中设定的部分)。
〇 TMS320F28335介绍
○ CMD文件(配置文件)
指定DSP内部的硬件存储器的一些相关地址以及长度。
包含两部分:MEMORY以及SECTIONS
MEMORY:指定DSP内部的ram和flash的首地址以及长度
SECTIONS:指定程序组成部分对应内存的储存部分(MEMORY中设定的部分)。
〇 TMS320F28335介绍










 〇 时钟与看门狗
〇 时钟与看门狗
 ● 内部时钟
● 内部时钟


 ❤ 2019.3.23
● 外设时钟
❤ 2019.3.23
● 外设时钟

 ● 看门狗
● 看门狗



 ● 时钟及看门狗寄存器(英文版System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide P34)(中文版见《手把手》P83)
● 时钟及看门狗寄存器(英文版System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide P34)(中文版见《手把手》P83)
 ♣ System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide:官方下载地址
● 关于看门狗及时钟的初始化例子
打开官方例程的时钟配置文件
♣ System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide:官方下载地址
● 关于看门狗及时钟的初始化例子
打开官方例程的时钟配置文件
 观察系统时钟初始化函数
观察系统时钟初始化函数


 如果需要启用watchdog,则用这个函数:
如果需要启用watchdog,则用这个函数:
 可以知道需要启用watchdog的话需要先后写入这两个值。
○ 下面是锁相环初始化
可以知道需要启用watchdog的话需要先后写入这两个值。
○ 下面是锁相环初始化
 首先看一下两个参数
首先看一下两个参数
 这个流程图配合寄存器说明来看
这个流程图配合寄存器说明来看


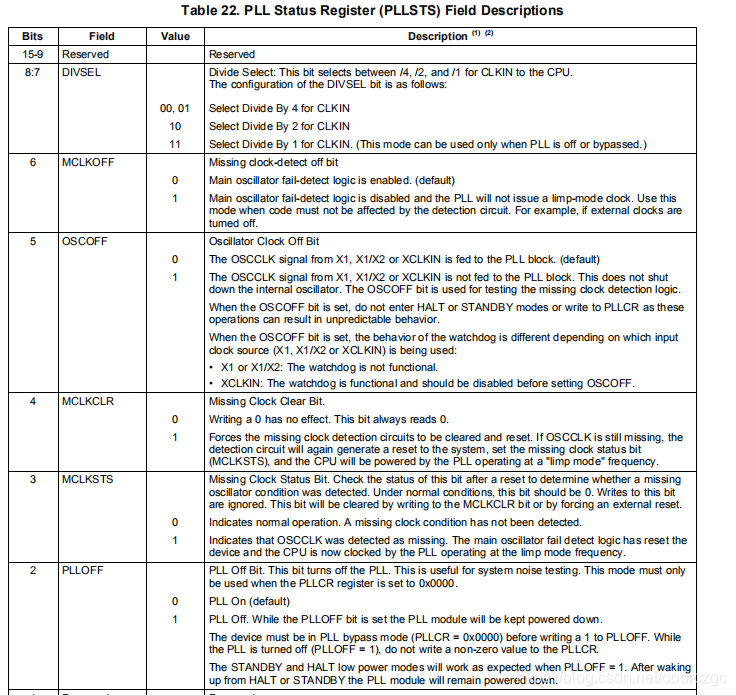
 稍微有点混乱,不过不需要看明白,反正用默认的就行,也就是10倍频,2分频,配合30M晶振,最后得到系统频率150M。
○ 初始化外设时钟
稍微有点混乱,不过不需要看明白,反正用默认的就行,也就是10倍频,2分频,配合30M晶振,最后得到系统频率150M。
○ 初始化外设时钟
 函数代码:
函数代码:
 原文地址:DSP的EALLOW和EDIS指令
先看这段:
原文地址:DSP的EALLOW和EDIS指令
先看这段:
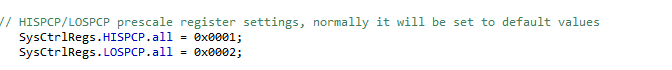 我们先找到对应的寄存器说明:
我们先找到对应的寄存器说明:
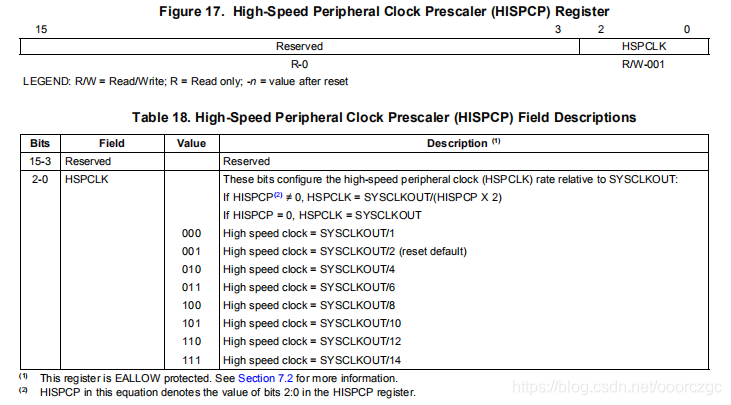
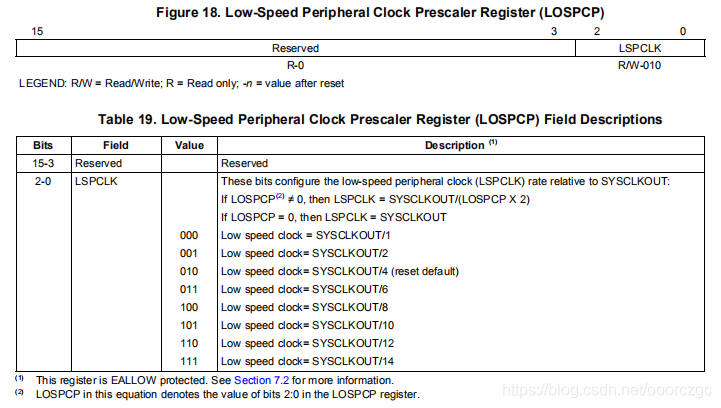 由上可知,这两句的意思是将高速时钟配置为2分频,将低速时钟配置为4分频。
由上可知,这两句的意思是将高速时钟配置为2分频,将低速时钟配置为4分频。
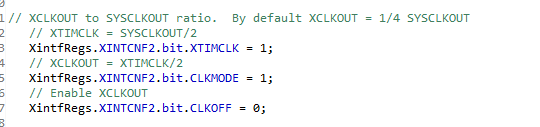 这个是用来控制时钟输出的,可以将时钟供给其他模块,可以省一个晶振(?)
这个是用来控制外设时钟的开关,需要哪个模块就开哪个时钟,不用就关上,可以省电。
这个是用来控制时钟输出的,可以将时钟供给其他模块,可以省一个晶振(?)
这个是用来控制外设时钟的开关,需要哪个模块就开哪个时钟,不用就关上,可以省电。



 〇 基础知识
● DSP的历史
略(自己看书百度去)
● 数字信号处理特点
〇 基础知识
● DSP的历史
略(自己看书百度去)
● 数字信号处理特点
 ● DSP主要特点
● DSP主要特点
 ● TI的芯片系列
● TI的芯片系列
 F28335系列属于C2000系列,在TI看来不属于DSP,属于MCU,但是我们就当成DSP学(?)
● C2000系列简介
F28335系列属于C2000系列,在TI看来不属于DSP,属于MCU,但是我们就当成DSP学(?)
● C2000系列简介
 ● DSP系统开发
● DSP系统开发
 ● 如何成为一个优秀的DSP工程师
● 如何成为一个优秀的DSP工程师
 (真的假的?)
● 教程总纲
(真的假的?)
● 教程总纲
 〇 DSP开发环境介绍
● CCS介绍
〇 DSP开发环境介绍
● CCS介绍
 ● CCS安装
(略)
● 仿真器
○ CCS6如何连接仿真器(这个手册上面有)
1、建立target configuration file
● CCS安装
(略)
● 仿真器
○ CCS6如何连接仿真器(这个手册上面有)
1、建立target configuration file
 2、输入名字
2、输入名字
 3、选择仿真器、芯片,然后点save
3、选择仿真器、芯片,然后点save
 ♣ 经常会在工程文件里生成一个target configuration 文件
♣ 经常会在工程文件里生成一个target configuration 文件
 ❤ 2019.3.22
〇 DSP开发流程
❤ 2019.3.22
〇 DSP开发流程

 ○ CMD文件(配置文件)
指定DSP内部的硬件存储器的一些相关地址以及长度。
包含两部分:MEMORY以及SECTIONS
MEMORY:指定DSP内部的ram和flash的首地址以及长度
SECTIONS:指定程序组成部分对应内存的储存部分(MEMORY中设定的部分)。
〇 TMS320F28335介绍
○ CMD文件(配置文件)
指定DSP内部的硬件存储器的一些相关地址以及长度。
包含两部分:MEMORY以及SECTIONS
MEMORY:指定DSP内部的ram和flash的首地址以及长度
SECTIONS:指定程序组成部分对应内存的储存部分(MEMORY中设定的部分)。
〇 TMS320F28335介绍










 〇 时钟与看门狗
〇 时钟与看门狗
 ● 内部时钟
● 内部时钟


 ❤ 2019.3.23
● 外设时钟
❤ 2019.3.23
● 外设时钟

 ● 看门狗
● 看门狗



 ● 时钟及看门狗寄存器(英文版System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide P34)(中文版见《手把手》P83)
● 时钟及看门狗寄存器(英文版System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide P34)(中文版见《手把手》P83)
 ♣ System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide:官方下载地址
● 关于看门狗及时钟的初始化例子
打开官方例程的时钟配置文件
♣ System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide:官方下载地址
● 关于看门狗及时钟的初始化例子
打开官方例程的时钟配置文件
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// InitSysCtrl:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This function initializes the System Control registers to a known state.
// - Disables the watchdog
// - Set the PLLCR for proper SYSCLKOUT frequency
// - Set the pre-scaler for the high and low frequency peripheral clocks
// - Enable the clocks to the peripherals
void InitSysCtrl(void)
{
// Disable the watchdog
DisableDog();
// Initialize the PLL control: PLLCR and DIVSEL
// DSP28_PLLCR and DSP28_DIVSEL are defined in DSP2833x_Examples.h
InitPll(DSP28_PLLCR,DSP28_DIVSEL);
// Initialize the peripheral clocks
InitPeripheralClocks();
}
○ 第一个

//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example: DisableDog:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This function disables the watchdog timer.
void DisableDog(void)
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.WDCR= 0x0068;
EDIS;
}
可以看到0x0068,转换成二进制就是0000 0000 0110 1000,查看watchdog的寄存器说明(英文版System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide P54)(中文版见《手把手》P88),可以知道其意义。

 如果需要启用watchdog,则用这个函数:
如果需要启用watchdog,则用这个函数:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example: ServiceDog:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This function resets the watchdog timer.
// Enable this function for using ServiceDog in the application
void ServiceDog(void)
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.WDKEY = 0x0055;
SysCtrlRegs.WDKEY = 0x00AA;
EDIS;
}
查看相应寄存器:
 可以知道需要启用watchdog的话需要先后写入这两个值。
○ 下面是锁相环初始化
可以知道需要启用watchdog的话需要先后写入这两个值。
○ 下面是锁相环初始化
 首先看一下两个参数
首先看一下两个参数
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Specify the PLL control register (PLLCR) and divide select (DIVSEL) value.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//#define DSP28_DIVSEL 0 // Enable /4 for SYSCLKOUT
//#define DSP28_DIVSEL 1 // Disable /4 for SYSCKOUT
#define DSP28_DIVSEL 2 // Enable /2 for SYSCLKOUT
//#define DSP28_DIVSEL 3 // Enable /1 for SYSCLKOUT
#define DSP28_PLLCR 10
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 9
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 8
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 7
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 6
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 5
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 4
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 3
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 2
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 1
//#define DSP28_PLLCR 0 // PLL is bypassed in this mode
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
可以看出DSP28_PLLCR是倍频,DSP28_DIVSEL是分频,然后在看一下倍频与分频设置函数:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example: InitPll:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This function initializes the PLLCR register.
void InitPll(Uint16 val, Uint16 divsel)
{
// Make sure the PLL is not running in limp mode
if (SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.MCLKSTS != 0)
{
// Missing external clock has been detected
// Replace this line with a call to an appropriate
// SystemShutdown(); function.
asm(" ESTOP0");
}
// DIVSEL MUST be 0 before PLLCR can be changed from
// 0x0000. It is set to 0 by an external reset XRSn
// This puts us in 1/4
if (SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.DIVSEL != 0)
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.DIVSEL = 0;
EDIS;
}
// Change the PLLCR
if (SysCtrlRegs.PLLCR.bit.DIV != val)
{
EALLOW;
// Before setting PLLCR turn off missing clock detect logic
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.MCLKOFF = 1;
SysCtrlRegs.PLLCR.bit.DIV = val;
EDIS;
// Optional: Wait for PLL to lock.
// During this time the CPU will switch to OSCCLK/2 until
// the PLL is stable. Once the PLL is stable the CPU will
// switch to the new PLL value.
//
// This time-to-lock is monitored by a PLL lock counter.
//
// Code is not required to sit and wait for the PLL to lock.
// However, if the code does anything that is timing critical,
// and requires the correct clock be locked, then it is best to
// wait until this switching has completed.
// Wait for the PLL lock bit to be set.
// The watchdog should be disabled before this loop, or fed within
// the loop via ServiceDog().
// Uncomment to disable the watchdog
DisableDog();
while(SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.PLLLOCKS != 1)
{
// Uncomment to service the watchdog
// ServiceDog();
}
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.MCLKOFF = 0;
EDIS;
}
// If switching to 1/2
if((divsel == 1)||(divsel == 2))
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.DIVSEL = divsel;
EDIS;
}
// If switching to 1/1
// * First go to 1/2 and let the power settle
// The time required will depend on the system, this is only an example
// * Then switch to 1/1
if(divsel == 3)
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.DIVSEL = 2;
DELAY_US(50L);
SysCtrlRegs.PLLSTS.bit.DIVSEL = 3;
EDIS;
}
}
有点乱,看不懂,但是ti贴心的(真的么?)画了个流程图:
 这个流程图配合寄存器说明来看
这个流程图配合寄存器说明来看



 稍微有点混乱,不过不需要看明白,反正用默认的就行,也就是10倍频,2分频,配合30M晶振,最后得到系统频率150M。
○ 初始化外设时钟
稍微有点混乱,不过不需要看明白,反正用默认的就行,也就是10倍频,2分频,配合30M晶振,最后得到系统频率150M。
○ 初始化外设时钟
 函数代码:
函数代码:
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example: InitPeripheralClocks:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This function initializes the clocks to the peripheral modules.
// First the high and low clock prescalers are set
// Second the clocks are enabled to each peripheral.
// To reduce power, leave clocks to unused peripherals disabled
//
// Note: If a peripherals clock is not enabled then you cannot
// read or write to the registers for that peripheral
void InitPeripheralClocks(void)
{
EALLOW;
// HISPCP/LOSPCP prescale register settings, normally it will be set to default values
SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = 0x0001;
SysCtrlRegs.LOSPCP.all = 0x0002;
// XCLKOUT to SYSCLKOUT ratio. By default XCLKOUT = 1/4 SYSCLKOUT
// XTIMCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2
XintfRegs.XINTCNF2.bit.XTIMCLK = 1;
// XCLKOUT = XTIMCLK/2
XintfRegs.XINTCNF2.bit.CLKMODE = 1;
// Enable XCLKOUT
XintfRegs.XINTCNF2.bit.CLKOFF = 0;
// Peripheral clock enables set for the selected peripherals.
// If you are not using a peripheral leave the clock off
// to save on power.
//
// Note: not all peripherals are available on all 2833x derivates.
// Refer to the datasheet for your particular device.
//
// This function is not written to be an example of efficient code.
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.ADCENCLK = 1; // ADC
// *IMPORTANT*
// The ADC_cal function, which copies the ADC calibration values from TI reserved
// OTP into the ADCREFSEL and ADCOFFTRIM registers, occurs automatically in the
// Boot ROM. If the boot ROM code is bypassed during the debug process, the
// following function MUST be called for the ADC to function according
// to specification. The clocks to the ADC MUST be enabled before calling this
// function.
// See the device data manual and/or the ADC Reference
// Manual for more information.
ADC_cal();
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.I2CAENCLK = 1; // I2C
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.SCIAENCLK = 1; // SCI-A
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.SCIBENCLK = 1; // SCI-B
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.SCICENCLK = 1; // SCI-C
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.SPIAENCLK = 1; // SPI-A
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.MCBSPAENCLK = 1; // McBSP-A
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.MCBSPBENCLK = 1; // McBSP-B
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.ECANAENCLK=1; // eCAN-A
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.ECANBENCLK=1; // eCAN-B
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0; // Disable TBCLK within the ePWM
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM1ENCLK = 1; // ePWM1
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM2ENCLK = 1; // ePWM2
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM3ENCLK = 1; // ePWM3
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM4ENCLK = 1; // ePWM4
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM5ENCLK = 1; // ePWM5
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM6ENCLK = 1; // ePWM6
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1; // Enable TBCLK within the ePWM
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP3ENCLK = 1; // eCAP3
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP4ENCLK = 1; // eCAP4
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP5ENCLK = 1; // eCAP5
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP6ENCLK = 1; // eCAP6
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP1ENCLK = 1; // eCAP1
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.ECAP2ENCLK = 1; // eCAP2
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EQEP1ENCLK = 1; // eQEP1
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EQEP2ENCLK = 1; // eQEP2
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.CPUTIMER0ENCLK = 1; // CPU Timer 0
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.CPUTIMER1ENCLK = 1; // CPU Timer 1
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.CPUTIMER2ENCLK = 1; // CPU Timer 2
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.DMAENCLK = 1; // DMA Clock
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.XINTFENCLK = 1; // XTIMCLK
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR3.bit.GPIOINENCLK = 1; // GPIO input clock
EDIS;
}
♣ 首先注意的是EALLOW和EDIS语句,关于这两个语句,我找到了一篇介绍:
 原文地址:DSP的EALLOW和EDIS指令
先看这段:
原文地址:DSP的EALLOW和EDIS指令
先看这段:
 我们先找到对应的寄存器说明:
我们先找到对应的寄存器说明:

 由上可知,这两句的意思是将高速时钟配置为2分频,将低速时钟配置为4分频。
由上可知,这两句的意思是将高速时钟配置为2分频,将低速时钟配置为4分频。
 这个是用来控制时钟输出的,可以将时钟供给其他模块,可以省一个晶振(?)
这个是用来控制外设时钟的开关,需要哪个模块就开哪个时钟,不用就关上,可以省电。
这个是用来控制时钟输出的,可以将时钟供给其他模块,可以省一个晶振(?)
这个是用来控制外设时钟的开关,需要哪个模块就开哪个时钟,不用就关上,可以省电。
