常见的交换排序包括冒泡排序和快速排序。
用于显示的代码:show.cpp

最好的情况下(排序前就已经有序),时间复杂度为:
#include cout << *(t+i) << endl;
}
冒泡排序
bubble.cpptemplate <class T>
int bubble_sort(T* t, int n)
{
int camp_times = 0;
for(int j=0; j1; j++)
{
for(int k=j+1; kif(t[j] > t[k])
{
T tmp = t[j];
t[j] = t[k];
t[k] = tmp;
}
}
}
return camp_times;
}
主函数:
#include "bubble.cpp"
#include "show.cpp"
int main()
{
double num[] = {1.2, 4.55, 2.34, 56.56, 78.3, -23.5, 9.8};
int numi[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
int n = 7;
cout << "--------------before--------------
";
showww(num, n);
int campare_times = bubble_sort(num,n);
cout << "--------------after--------------
";
showww(num,n);
cout << "---------compare_times: " << campare_times << "---------
" << endl;
cout << "--------------before--------------
";
showww(numi, n);
campare_times = bubble_sort(numi,n);
cout << "--------------after--------------
";
showww(numi,n);
cout << "---------compare_times: " << campare_times << "---------" << endl;
return 0;
}
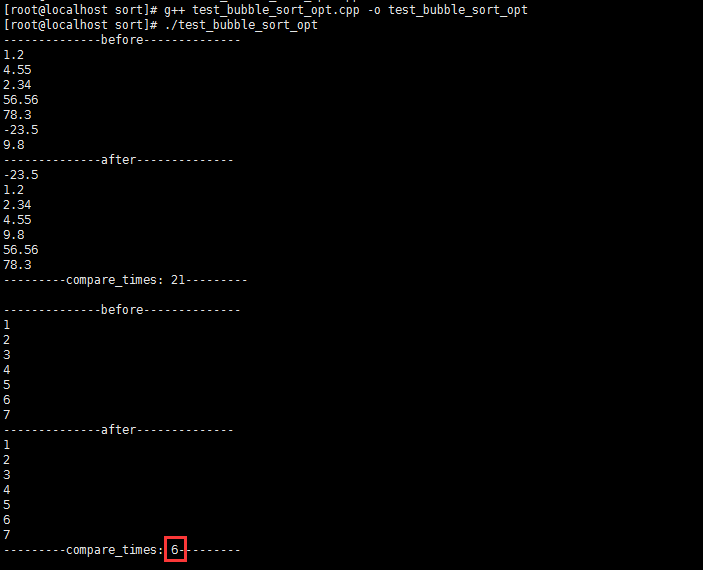
执行结果: 
时间复杂度
o(n2)
空间复杂度
o(1)
空间复杂度不受问题规模影响,为就地排序。
优化后的冒泡排序
优化原理:当某一次排序不再发生冒泡(大小交换)时,说明已经有序了,则不再进行下一轮排序。最好的情况下(排序前就已经有序),时间复杂度为:
bubble_sort.cppo(n)
template <class T>
int bubble_sort(T* t, int n)
{
int camp_times = 0;
bool exchange = false;
for(int j=0; j1; j++)
{
for(int k=j+1; kif(t[j] > t[k])
{
T tmp = t[j];
t[j] = t[k];
t[k] = tmp;
exchange = true;
}
}
if(!exchange)
break;
}
return camp_times;
}
执行结果: 