又是十二点了,但是很兴奋,因为从这节课开始,我们将会进行F28027一系列的动手实践练习,深入了解一门技术的唯一办法就是多动手实践,多总结反思。
来来来,不扯了,直接开始了。
在正式开始写程序前,我们还有一个问题要解决,那就是CCS5.4默认输出的是.out文件,而我们DSP Proteus仿真需要的是cof文件,所以我们还需要继续设置下CCS工程的属性。
我们在第一节课的时候,已经教大家如何创建一个空的工程,我们直接在那个工程的基础上进行修改。
1、生成hex文件
右键工程名,选择Properties,进去之后,在Build里面,有个Steps-Apply Predefined Step,在下拉框里面选择hex文件
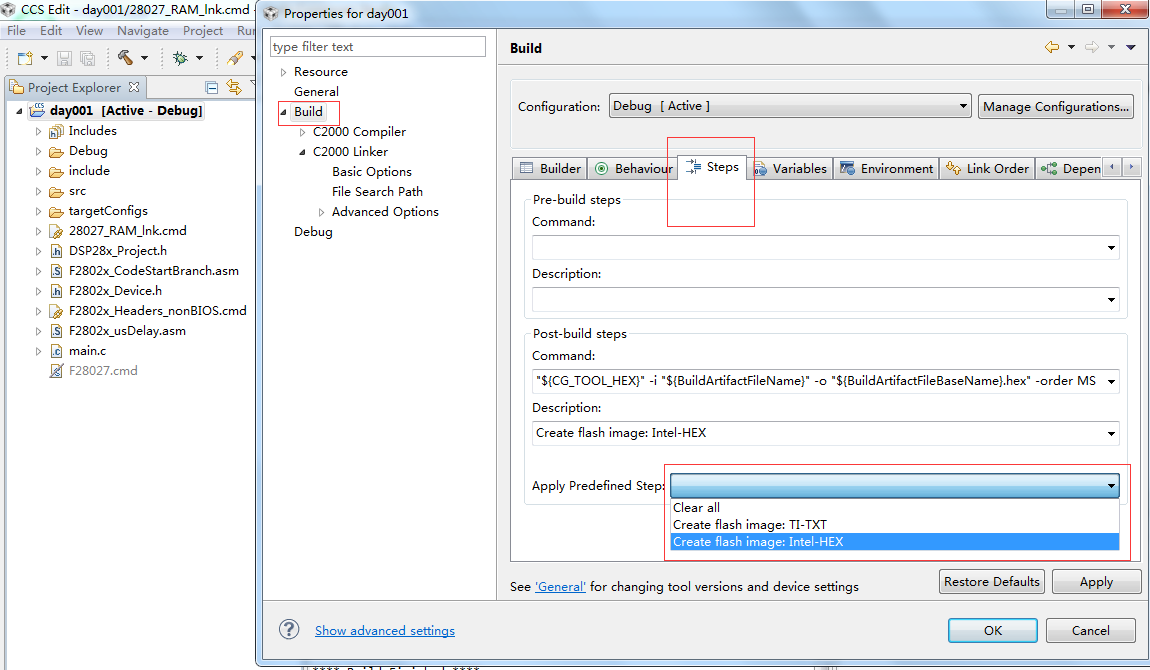
2、生成cof文件
右键工程名,选择Properties,进去之后,在Build-C2000 Linker-Basic Options里面,out file nameg改成”${ProjName}.cof”
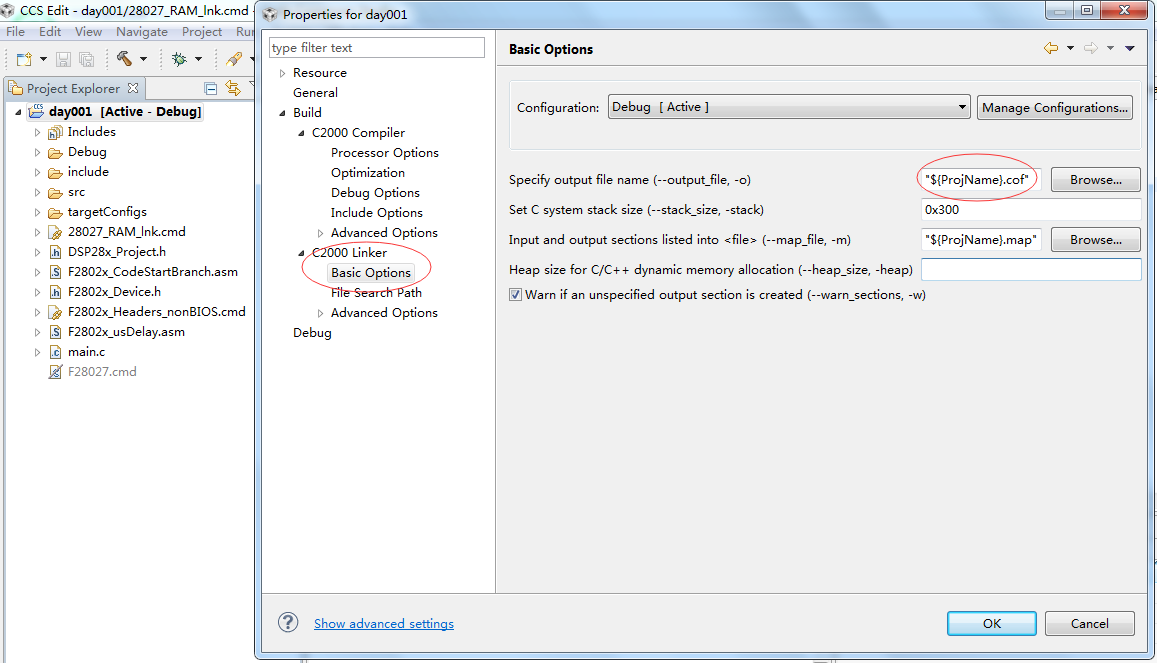
好了,实践之前的准备工作已经都完成了,现在正式开始实践课程。
实践课程主要分为两部分:仿真环境搭建和软件代码编写。
对于仿真环境搭建,我们只说一遍,因为这个东西只要环境搭建好了,后续的实践课稍微调整下电路就行了,没太大的必要每节课都说。
硬件环境搭建
1、新建工程
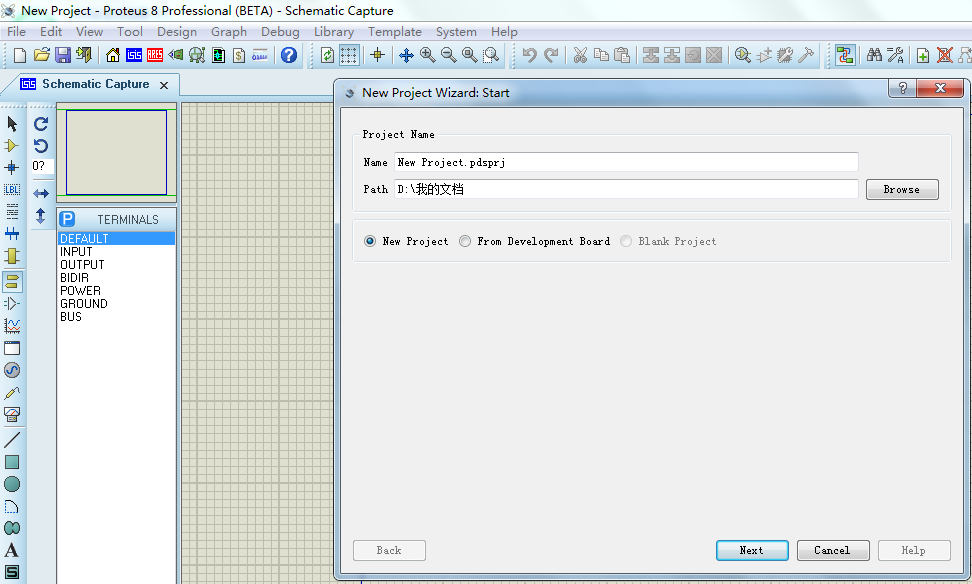
新建工程,如图所示,不停的下一步下一步,建一个空的工程。
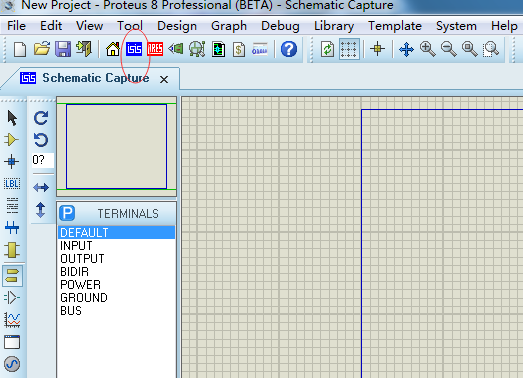
2、新建Schematic Capture文件
直接点击工具栏的ISIS蓝 {MOD}底纹的图标即可
3、在仿真库中挑选所需要的器件
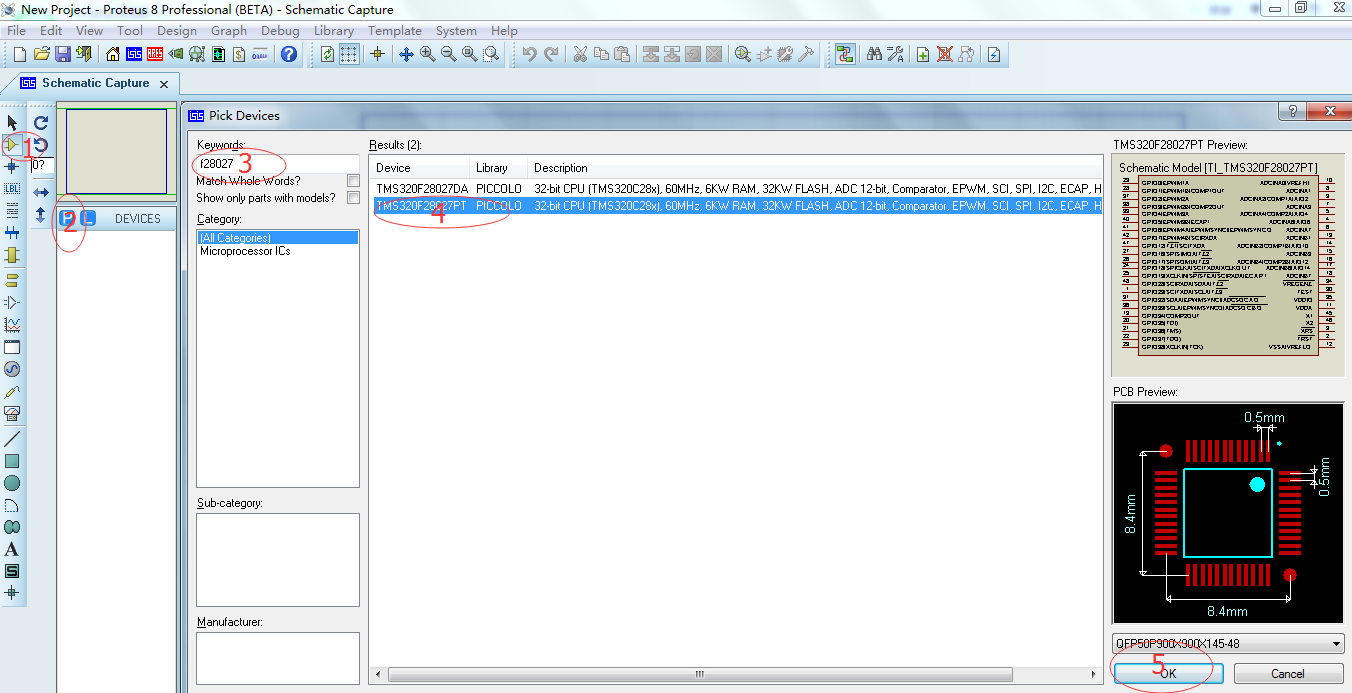
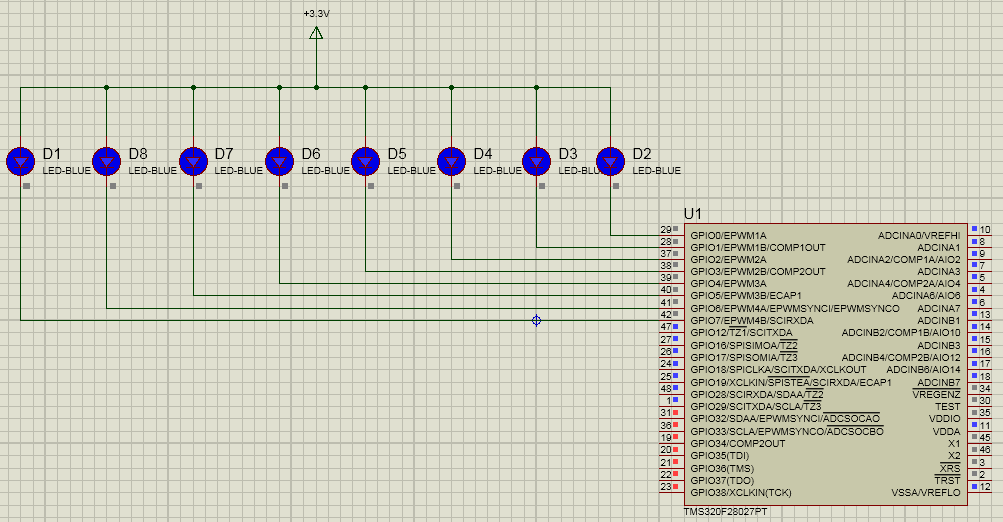
选择器件的顺序如图里面的圈圈序号所示,在本次实践课中,我们需要F28027芯片、LED。
4、画仿真图
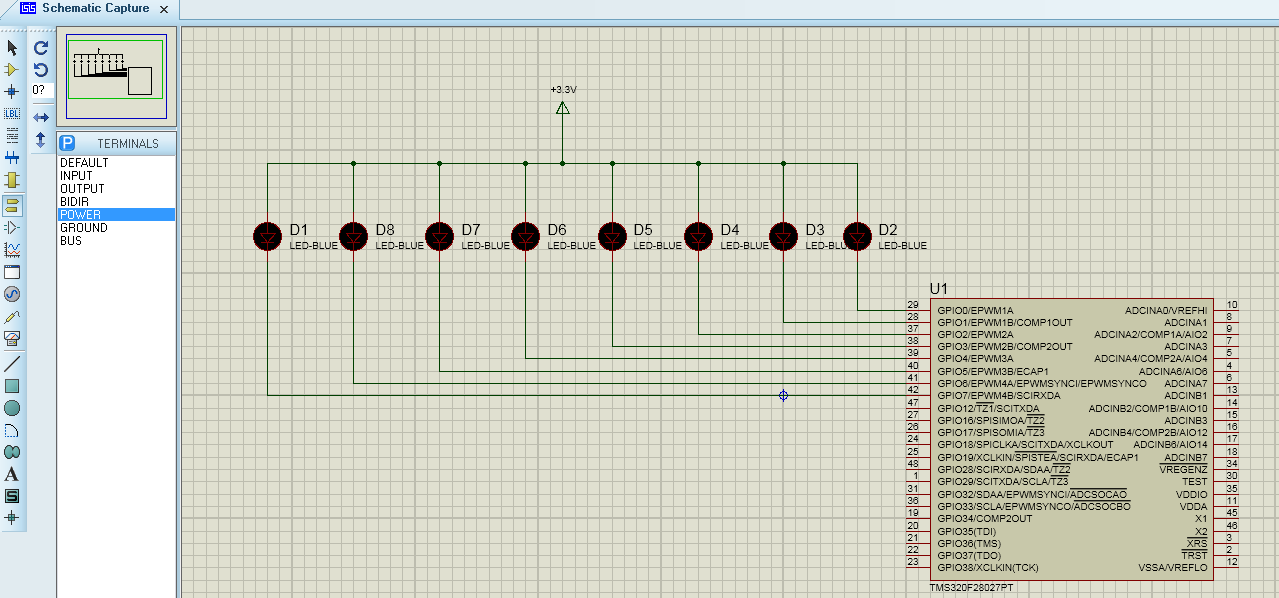
画好的仿真图如上所示。
5、指定仿真所需要的cof可执行文件
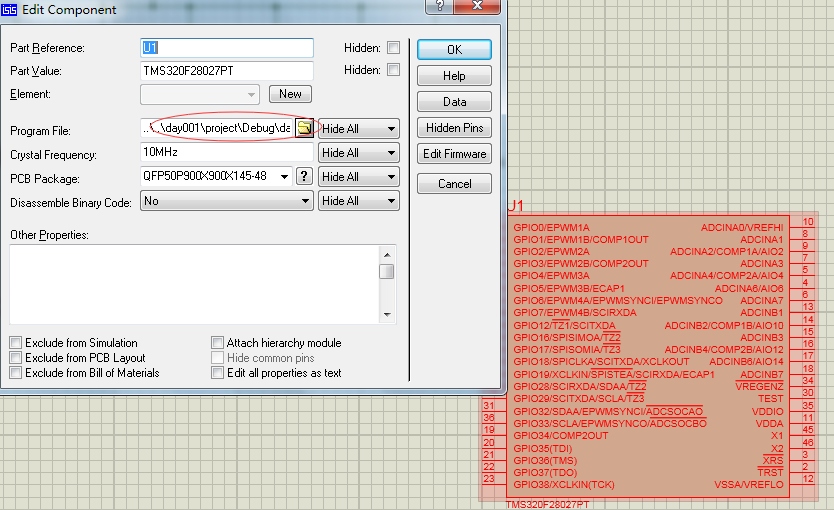
如图圈圈所示,圈圈里面有个文件夹图标,点进去选择到我们最开始设置的那个空工程的cof文件。
硬件仿真环境已经设置完成,由于cof文件我们也选好了,后续完成软件编写编译后,直接点击左下角的开始键进行系统仿真功能仿真。
硬件环境已经OK,现在重点说软件编程部分了。
要开始动手写之前,我们要先理清楚F28027程序的开发流程:
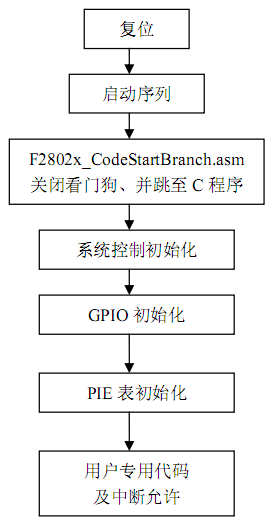
前面部分,包括F2802x_CodeStartBranch.asm文件,已经都有了,而且我们在前面的课程中,也基本都把这些东西给讲到了,至于CMD文件,TI已经提供了非常标准的链接文件,也是不用我们再另外去写,直接使用就行了,我们只要理解里面的代码含义,然后借用,做最高效的开发。我们唯一要做的就是用到什么文件或者功能,就修改对应的文件,其他的全部保持不变就行了。
既然我们这节课是LED流水灯,那肯定要用GPIO端口去输出高低电平去控制,所以需要GPIO控制文件F2802x_Gpio.c,把C: icontrolSUITEdevice_supportf2802xv200f2802x_commonsource路径下的F2802x_Gpio.c文件拷贝到
D:studyday001projectsrc路径下。
从上面的硬件环境中可以看到,我们要把GPIO0-GPIO7设置为GPIO输出端口,当输出低电平时,LED亮,输出高电平时,LED灭。
目的很明确了,那我们就去GPIO.c文件里面进行相应的设置操作:
1、选择GPIO0-GPIO7为普通GPIO引脚;
2、设置引脚为输出引脚;
3、输入鉴定滤波与SYSCLKOUT同步;
4、使能上拉电阻;
代码如下:
可以看到流水灯以1ms的频率进行闪烁,达到本次课程的预期效果,真高兴,看来前面几节课的基础确实很重要,只要把思路理清楚了,程序还是比较简单的,现在一点半了,明天希望可以搞到12864那里,呵呵,现在洗洗睡了,最近几天白天状态都不怎么好,示例程序我会传到CSDN下载库和qq群里面。
菜鸟交流qq群107691092
来来来,不扯了,直接开始了。
在正式开始写程序前,我们还有一个问题要解决,那就是CCS5.4默认输出的是.out文件,而我们DSP Proteus仿真需要的是cof文件,所以我们还需要继续设置下CCS工程的属性。
我们在第一节课的时候,已经教大家如何创建一个空的工程,我们直接在那个工程的基础上进行修改。
1、生成hex文件
右键工程名,选择Properties,进去之后,在Build里面,有个Steps-Apply Predefined Step,在下拉框里面选择hex文件

2、生成cof文件
右键工程名,选择Properties,进去之后,在Build-C2000 Linker-Basic Options里面,out file nameg改成”${ProjName}.cof”

好了,实践之前的准备工作已经都完成了,现在正式开始实践课程。
实践课程主要分为两部分:仿真环境搭建和软件代码编写。
对于仿真环境搭建,我们只说一遍,因为这个东西只要环境搭建好了,后续的实践课稍微调整下电路就行了,没太大的必要每节课都说。
硬件环境搭建
1、新建工程

新建工程,如图所示,不停的下一步下一步,建一个空的工程。
2、新建Schematic Capture文件
直接点击工具栏的ISIS蓝 {MOD}底纹的图标即可

3、在仿真库中挑选所需要的器件

选择器件的顺序如图里面的圈圈序号所示,在本次实践课中,我们需要F28027芯片、LED。
4、画仿真图

画好的仿真图如上所示。
5、指定仿真所需要的cof可执行文件

如图圈圈所示,圈圈里面有个文件夹图标,点进去选择到我们最开始设置的那个空工程的cof文件。
硬件仿真环境已经设置完成,由于cof文件我们也选好了,后续完成软件编写编译后,直接点击左下角的开始键进行系统仿真功能仿真。
硬件环境已经OK,现在重点说软件编程部分了。
要开始动手写之前,我们要先理清楚F28027程序的开发流程:

前面部分,包括F2802x_CodeStartBranch.asm文件,已经都有了,而且我们在前面的课程中,也基本都把这些东西给讲到了,至于CMD文件,TI已经提供了非常标准的链接文件,也是不用我们再另外去写,直接使用就行了,我们只要理解里面的代码含义,然后借用,做最高效的开发。我们唯一要做的就是用到什么文件或者功能,就修改对应的文件,其他的全部保持不变就行了。
既然我们这节课是LED流水灯,那肯定要用GPIO端口去输出高低电平去控制,所以需要GPIO控制文件F2802x_Gpio.c,把C: icontrolSUITEdevice_supportf2802xv200f2802x_commonsource路径下的F2802x_Gpio.c文件拷贝到
D:studyday001projectsrc路径下。
从上面的硬件环境中可以看到,我们要把GPIO0-GPIO7设置为GPIO输出端口,当输出低电平时,LED亮,输出高电平时,LED灭。
目的很明确了,那我们就去GPIO.c文件里面进行相应的设置操作:
1、选择GPIO0-GPIO7为普通GPIO引脚;
2、设置引脚为输出引脚;
3、输入鉴定滤波与SYSCLKOUT同步;
4、使能上拉电阻;
代码如下:
void InitGpio(void)
{
EALLOW;
// Each GPIO pin can be:
// a) a GPIO input/output
// b) peripheral function 1
// c) peripheral function 2
// d) peripheral function 3
// By default, all are GPIO Inputs
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.all = 0x0000; // GPIO functionality GPIO0-GPIO15
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX2.all = 0x0000; // GPIO functionality GPIO16-GPIO31
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBMUX1.all = 0x0000; // GPIO functionality GPIO32-GPIO34
GpioCtrlRegs.AIOMUX1.all = 0x0000; // Dig.IO funct. applies to AIO2,4,6,10,12,14
GpioCtrlRegs.GPADIR.all = 0xFFFFFFFF; // GPIO0-GPIO31 are GP outputs
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.all = 0x0000; // GPIO32-GPIO34 are inputs
GpioCtrlRegs.AIODIR.all = 0x0000; // AIO2,4,6,19,12,14 are digital inputs
// Each input can have different qualification
// a) input synchronized to SYSCLKOUT
// b) input qualified by a sampling window
// c) input sent asynchronously (valid for peripheral inputs only)
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAQSEL1.all = 0x0000; // GPIO0-GPIO15 Synch to SYSCLKOUT
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAQSEL2.all = 0x0000; // GPIO16-GPIO31 Synch to SYSCLKOUT
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBQSEL1.all = 0x0000; // GPIO32-GPIO34 Synch to SYSCLKOUT
// Pull-ups can be enabled or disabled.
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAPUD.all = 0x0000; // Pullup's enabled GPIO0-GPIO31
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBPUD.all = 0x0000; // Pullup's enabled GPIO32-GPIO34
//GpioCtrlRegs.GPAPUD.all = 0xFFFF; // Pullup's disabled GPIO0-GPIO31
//GpioCtrlRegs.GPBPUD.all = 0xFFFF; // Pullup's disabled GPIO32-GPIO34
EDIS;
}
GPIO.c文件设置完之后,去main.c主函数里面,给GPIO0-GPIO7一个初始值,然后用翻转寄存器进行GPADAT值的变换,代码如下:
void main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2802x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2802x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
InitGpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2802x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2802x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2802x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2802x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
// Step 5. User specific code:
GpioDataRegs.GPADAT.all = 0x00000000; //GPIO0-GPIO31 initial value are 0
while(1)
{
GpioDataRegs.GPATOGGLE.all=0x000000ff;
DELAY_US(1000);
}
}
写完之后进行编译,生成cof文件,在仿真环境里面点击运行 
可以看到流水灯以1ms的频率进行闪烁,达到本次课程的预期效果,真高兴,看来前面几节课的基础确实很重要,只要把思路理清楚了,程序还是比较简单的,现在一点半了,明天希望可以搞到12864那里,呵呵,现在洗洗睡了,最近几天白天状态都不怎么好,示例程序我会传到CSDN下载库和qq群里面。
菜鸟交流qq群107691092