转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_23547831/article/details/51487978
前面我们讲解了系统截屏按键处理流程,HOME按键处理流程,今天再来讲解一下电源开关机按键事件流程,当然这也是系统按键处理流程方面的最后一篇博客了。
和截屏按键、HOME按键的处理流程类似,电源按键由于也是系统级别的按键,所以对其的事件处理逻辑是和截屏按键、HOME按键类似,不在某一个App中,而是在PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandledKey方法中。所以和前面两篇类似,这里我们也是从PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandledKey方法开始我们今天电源开关机按键的事件流程分析。
下面首先看一下dispatchUnhandledKey方法的实现逻辑:
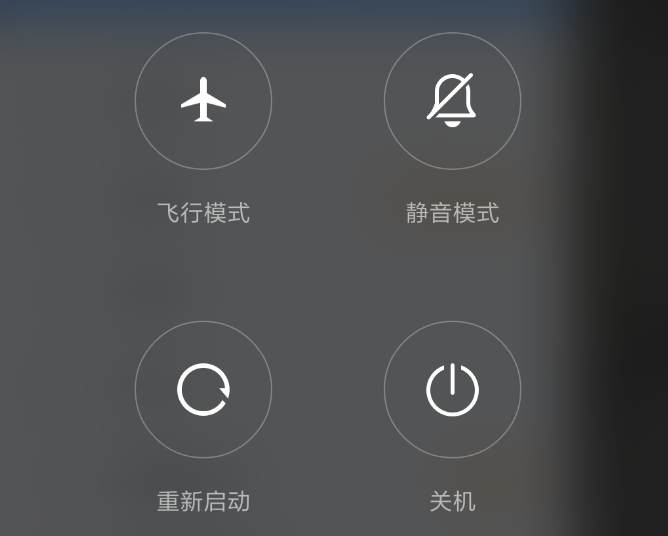 然后第三第四个case分之则是直接调用关机方法,这里我们先看第二个case,看看系统是如何显示出关机操作界面的。那我们看一下showGlobalActionsInternal方法的实现逻辑。
然后第三第四个case分之则是直接调用关机方法,这里我们先看第二个case,看看系统是如何显示出关机操作界面的。那我们看一下showGlobalActionsInternal方法的实现逻辑。
public KeyEvent dispatchUnhandledKey(WindowState win, KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {
...
KeyEvent fallbackEvent = null;
if ((event.getFlags() & KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK) == 0) {
final KeyCharacterMap kcm = event.getKeyCharacterMap();
final int keyCode = event.getKeyCode();
final int metaState = event.getMetaState();
final boolean initialDown = event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0;
// Check for fallback actions specified by the key character map.
final FallbackAction fallbackAction;
if (initialDown) {
fallbackAction = kcm.getFallbackAction(keyCode, metaState);
} else {
fallbackAction = mFallbackActions.get(keyCode);
}
if (fallbackAction != null) {
if (DEBUG_INPUT) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Fallback: keyCode=" + fallbackAction.keyCode
+ " metaState=" + Integer.toHexString(fallbackAction.metaState));
}
final int flags = event.getFlags() | KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK;
fallbackEvent = KeyEvent.obtain(
event.getDownTime(), event.getEventTime(),
event.getAction(), fallbackAction.keyCode,
event.getRepeatCount(), fallbackAction.metaState,
event.getDeviceId(), event.getScanCode(),
flags, event.getSource(), null);
if (!interceptFallback(win, fallbackEvent, policyFlags)) {
fallbackEvent.recycle();
fallbackEvent = null;
}
if (initialDown) {
mFallbackActions.put(keyCode, fallbackAction);
} else if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
mFallbackActions.remove(keyCode);
fallbackAction.recycle();
}
}
}
...
return fallbackEvent;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
private boolean interceptFallback(WindowState win, KeyEvent fallbackEvent, int policyFlags) {
int actions = interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(fallbackEvent, policyFlags);
if ((actions & ACTION_PASS_TO_USER) != 0) {
long delayMillis = interceptKeyBeforeDispatching(
win, fallbackEvent, policyFlags);
if (delayMillis == 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
public int interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {
...
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_POWER: {
result &= ~ACTION_PASS_TO_USER;
isWakeKey = false; // wake-up will be handled separately
if (down) {
interceptPowerKeyDown(event, interactive);
} else {
interceptPowerKeyUp(event, interactive, canceled);
}
break;
}
...
return result;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
private void interceptPowerKeyDown(KeyEvent event, boolean interactive) {
...
// Latch power key state to detect screenshot chord.
if (interactive && !mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTriggered
&& (event.getFlags() & KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK) == 0) {
mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTriggered = true;
mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTime = event.getDownTime();
interceptScreenshotChord();
}
// Stop ringing or end call if configured to do so when power is pressed.
TelecomManager telecomManager = getTelecommService();
boolean hungUp = false;
if (telecomManager != null) {
if (telecomManager.isRinging()) {
// Pressing Power while there's a ringing incoming
// call should silence the ringer.
telecomManager.silenceRinger();
} else if ((mIncallPowerBehavior
& Settings.Secure.INCALL_POWER_BUTTON_BEHAVIOR_HANGUP) != 0
&& telecomManager.isInCall() && interactive) {
// Otherwise, if "Power button ends call" is enabled,
// the Power button will hang up any current active call.
hungUp = telecomManager.endCall();
}
}
// If the power key has still not yet been handled, then detect short
// press, long press, or multi press and decide what to do.
mPowerKeyHandled = hungUp || mScreenshotChordVolumeDownKeyTriggered
|| mScreenshotChordVolumeUpKeyTriggered;
if (!mPowerKeyHandled) {
if (interactive) {
// When interactive, we're already awake.
// Wait for a long press or for the button to be released to decide what to do.
if (hasLongPressOnPowerBehavior()) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS);
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,
ViewConfiguration.get(mContext).getDeviceGlobalActionKeyTimeout());
}
} else {
wakeUpFromPowerKey(event.getDownTime());
if (mSupportLongPressPowerWhenNonInteractive && hasLongPressOnPowerBehavior()) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS);
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,
ViewConfiguration.get(mContext).getDeviceGlobalActionKeyTimeout());
mBeganFromNonInteractive = true;
} else {
final int maxCount = getMaxMultiPressPowerCount();
if (maxCount <= 1) {
mPowerKeyHandled = true;
} else {
mBeganFromNonInteractive = true;
}
}
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
case MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS:
powerLongPress();
break;- 1
- 2
- 3
private void powerLongPress() {
final int behavior = getResolvedLongPressOnPowerBehavior();
switch (behavior) {
case LONG_PRESS_POWER_NOTHING:
break;
case LONG_PRESS_POWER_GLOBAL_ACTIONS:
mPowerKeyHandled = true;
if (!performHapticFeedbackLw(null, HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS, false)) {
performAuditoryFeedbackForAccessibilityIfNeed();
}
showGlobalActionsInternal();
break;
case LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF:
case LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF_NO_CONFIRM:
mPowerKeyHandled = true;
performHapticFeedbackLw(null, HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS, false);
sendCloseSystemWindows(SYSTEM_DIALOG_REASON_GLOBAL_ACTIONS);
mWindowManagerFuncs.shutdown(behavior == LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF);
break;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
 然后第三第四个case分之则是直接调用关机方法,这里我们先看第二个case,看看系统是如何显示出关机操作界面的。那我们看一下showGlobalActionsInternal方法的实现逻辑。
然后第三第四个case分之则是直接调用关机方法,这里我们先看第二个case,看看系统是如何显示出关机操作界面的。那我们看一下showGlobalActionsInternal方法的实现逻辑。
void showGlobalActionsInternal() {
sendCloseSystemWindows(SYSTEM_DIALOG_REASON_GLOBAL_ACTIONS);
if (mGlobalActions == null) {
mGlobalActions = new GlobalActions(mContext, mWindowManagerFuncs);
}
final boolean keyguardShowing = isKeyguardShowingAndNotOccluded();
mGlobalActions.showDialog(keyguardShowing, isDeviceProvisioned());
if (keyguardShowing) {
// since it took two seconds of long press to bring this up,
// poke the wake lock so they have some time to see the dialog.
mPowerManager.userActivity(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), false);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
public GlobalActions(Context context, WindowManagerFuncs windowManagerFuncs) {
mContext = context;
mWindowManagerFuncs = windowManagerFuncs;
mAudioManager = (AudioManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
mDreamManager = IDreamManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(DreamService.DREAM_SERVICE));
// receive broadcasts
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_CLOSE_SYSTEM_DIALOGS);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_OFF);
filter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_EMERGENCY_CALLBACK_MODE_CHANGED);
context.registerReceiver(mBroadcastReceiver, filter);
ConnectivityManager cm = (ConnectivityManager)
context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
mHasTelephony = cm.isNetworkSupported(ConnectivityManager.TYPE_MOBILE);
// get notified of phone state changes
TelephonyManager telephonyManager =
(TelephonyManager) context.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
telephonyManager.listen(mPhoneStateListener, PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_SERVICE_STATE);
mContext.getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(
Settings.Global.getUriFor(Settings.Global.AIRPLANE_MODE_ON), true,
mAirplaneModeObserver);
Vibrator vibrator = (Vibrator) mContext.getSystemService(Context.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
mHasVibrator = vibrator != null && vibrator.hasVibrator();
mShowSilentToggle = SHOW_SILENT_TOGGLE && !mContext.getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_useFixedVolume);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
public void showDialog(boolean keyguardShowing, boolean isDeviceProvisioned) {
mKeyguardShowing = keyguardShowing;
mDeviceProvisioned = isDeviceProvisioned;
if (mDialog != null) {
mDialog.dismiss();
mDialog = null;
// Show delayed, so that the dismiss of the previous dialog completes
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MESSAGE_SHOW);
} else {
handleShow();
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
private void handleShow() {
awakenIfNecessary();
mDialog = createDialog();
prepareDialog();
// If we only have 1 item and it's a simple press action, just do this action.
if (mAdapter.getCount() == 1
&& mAdapter.getItem(0) instanceof SinglePressAction
&& !(mAdapter.getItem(0) instanceof LongPressAction)) {
((SinglePressAction) mAdapter.getItem(0)).onPress();
} else {
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs = mDialog.getWindow().getAttributes();
attrs.setTitle("GlobalActions");
mDialog.getWindow().setAttributes(attrs);
mDialog.show();
mDialog.getWindow().getDecorView().setSystemUiVisibility(View.STATUS_BAR_DISABLE_EXPAND);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
private GlobalActionsDialog createDialog() {
...
mAirplaneModeOn = new ToggleAction(
R.drawable.ic_lock_airplane_mode,
R.drawable.ic_lock_airplane_mode_off,
R.string.global_actions_toggle_airplane_mode,
R.string.global_actions_airplane_mode_on_status,
R.string.global_actions_airplane_mode_off_status) {
void onToggle(boolean on) {
if (mHasTelephony && Boolean.parseBoolean(
SystemProperties.get(TelephonyProperties.PROPERTY_INECM_MODE))) {
mIsWaitingForEcmExit = true;
// Launch ECM exit dialog
Intent ecmDialogIntent =
new Intent(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SHOW_NOTICE_ECM_BLOCK_OTHERS, null);
ecmDialogIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mContext.startActivity(ecmDialogIntent);
} else {
changeAirplaneModeSystemSetting(on);
}
}
@Override
protected void changeStateFromPress(boolean buttonOn) {
if (!mHasTelephony) return;
// In ECM mode airplane state cannot be changed
if (!(Boolean.parseBoolean(
SystemProperties.get(TelephonyProperties.PROPERTY_INECM_MODE)))) {
mState = buttonOn ? State.TurningOn : State.TurningOff;
mAirplaneState = mState;
}
}
public boolean showDuringKeyguard() {
return true;
}
public boolean showBeforeProvisioning() {
return false;
}
};
onAirplaneModeChanged();
mItems = new ArrayList();
String[] defaultActions = mContext.getResources().getStringArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.config_globalActionsList);
ArraySet addedKeys = new ArraySet();
for (int i = 0; i < defaultActions.length; i++) {
String actionKey = defaultActions[i];
if (addedKeys.contains(actionKey)) {
// If we already have added this, don't add it again.
continue;
}
if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_POWER.equals(actionKey)) {
mItems.add(new PowerAction());
} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_AIRPLANE.equals(actionKey)) {